Unveiling the Secrets of the pH Scale: A Journey Through Everyday Acidity and Alkalinity
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the pH Scale: A Journey Through Everyday Acidity and Alkalinity
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of the pH Scale: A Journey Through Everyday Acidity and Alkalinity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of the pH Scale: A Journey Through Everyday Acidity and Alkalinity

The pH scale, a seemingly simple numerical system, holds the key to understanding the acidic or alkaline nature of countless substances in our world. From the tangy bite of lemon juice to the soothing properties of baking soda, each substance possesses a unique pH value that influences its properties and interactions. This article delves into the fascinating world of the pH scale, exploring its significance through everyday examples and highlighting its vital role in various aspects of our lives.
Understanding the pH Scale: A Numerical Compass for Acidity and Alkalinity
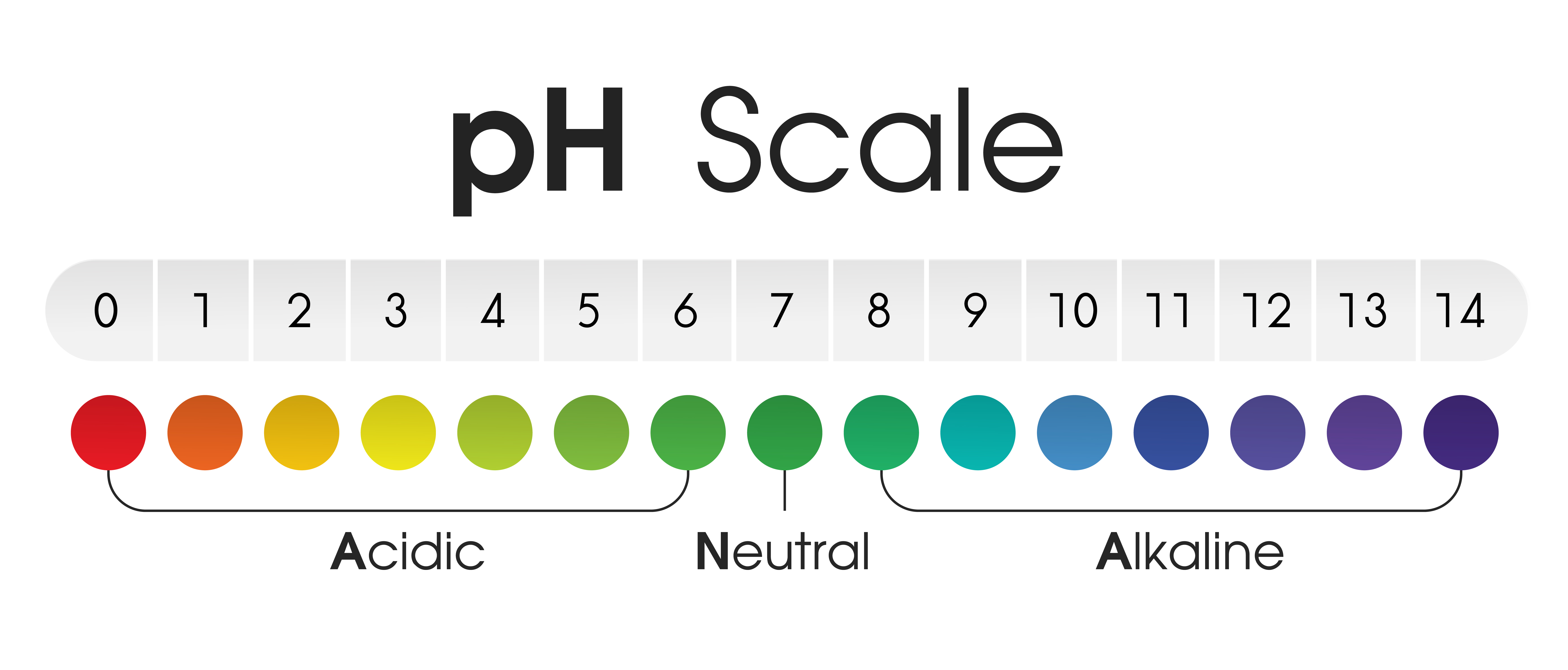
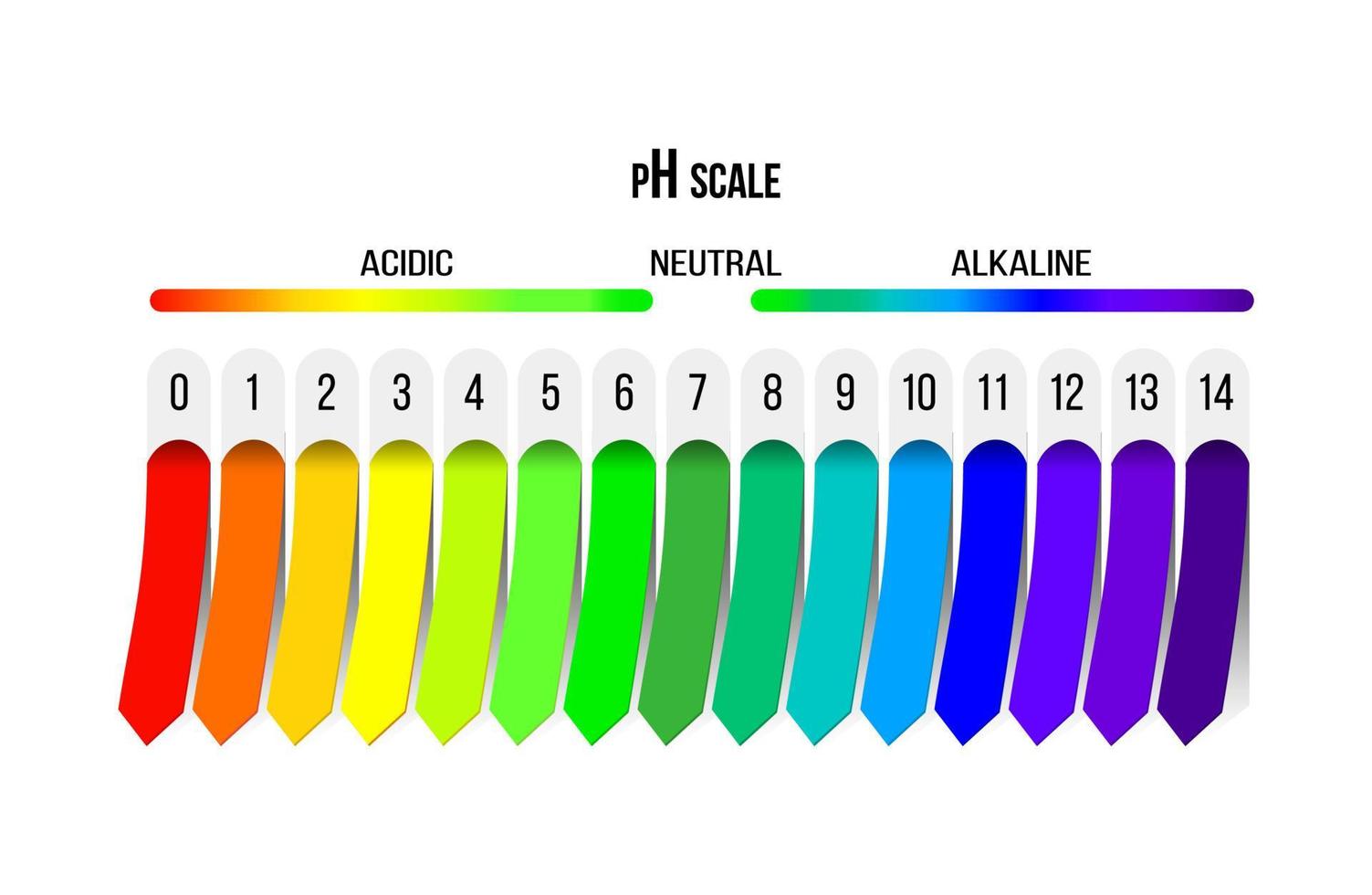
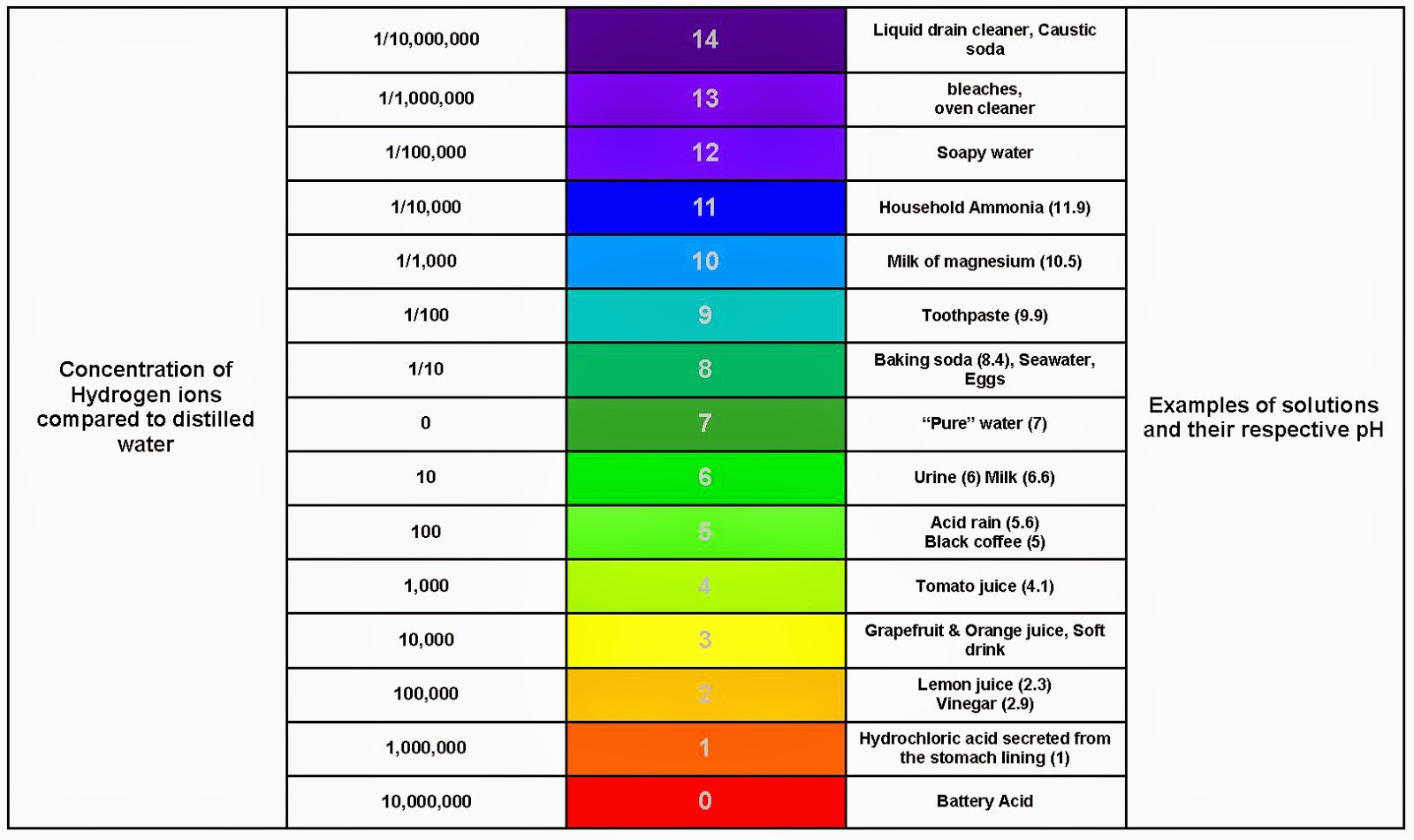
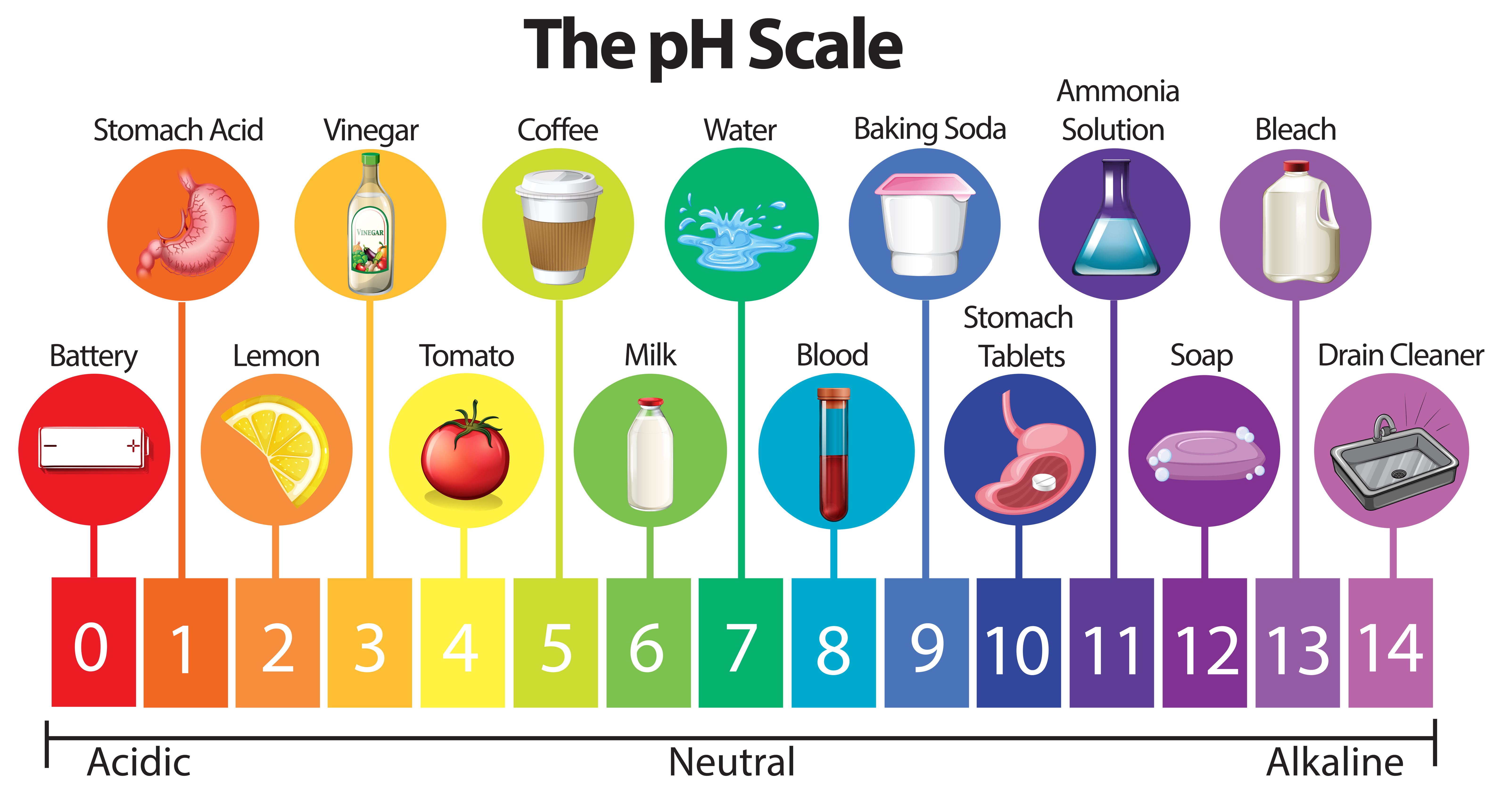
The pH scale, ranging from 0 to 14, serves as a numerical compass to navigate the spectrum of acidity and alkalinity. A pH of 7 represents neutrality, with values below 7 indicating increasing acidity and values above 7 denoting increasing alkalinity. This scale is logarithmic, meaning that each whole number change represents a tenfold difference in hydrogen ion concentration.
Examples of Everyday Substances on the pH Scale:
Highly Acidic (pH 0-3):
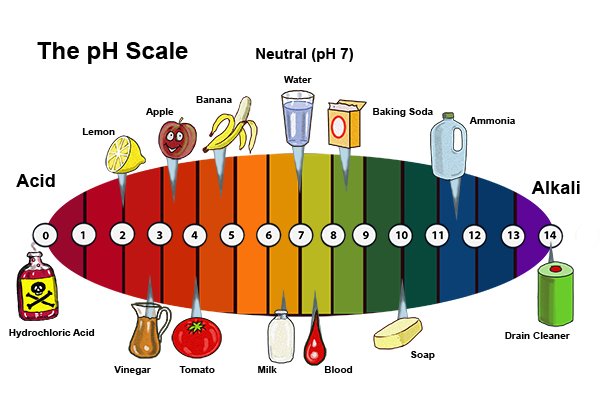
- Stomach Acid: The potent digestive fluid in our stomachs boasts a pH of 1-3, facilitating the breakdown of food. Its high acidity is essential for protein digestion and killing harmful bacteria.
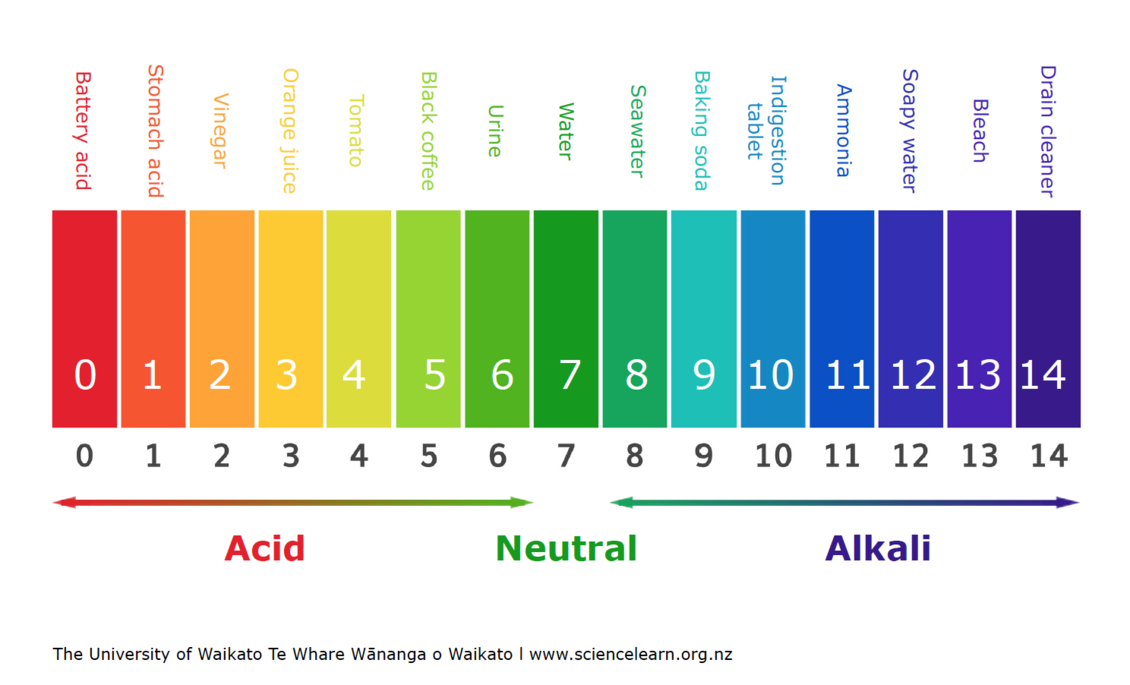
- Battery Acid: Used in car batteries, this corrosive liquid boasts a pH of 0-1, showcasing its extreme acidic nature.
- Lemon Juice: This tart citrus juice, with a pH of 2-3, adds a tangy flavor to various dishes and beverages.
Moderately Acidic (pH 4-6):
- Vinegar: This common household ingredient, with a pH of 3-4, adds a sour taste to salads and marinades.
- Coffee: This popular beverage, boasting a pH of 4-5, offers a stimulating caffeine kick.
- Black Tea: This aromatic beverage, with a pH of 4-6, provides a mild, slightly acidic taste.
Neutral (pH 7):
- Pure Water: The benchmark for neutrality, pure water possesses a pH of 7, showcasing its balanced nature.
- Human Blood: Maintaining a precise pH of 7.35-7.45 is crucial for human health, highlighting the importance of blood’s neutral pH.
Moderately Alkaline (pH 8-10):
- Baking Soda: This versatile household staple, with a pH of 8-9, acts as a leavening agent in baking and a mild cleaning agent.
- Seawater: This salty liquid, with a pH of 8-8.5, provides a habitat for diverse marine life.
- Milk: This dairy product, with a pH of 6.5-6.7, provides essential nutrients and calcium.
Highly Alkaline (pH 11-14):
- Ammonia: This pungent cleaning agent, with a pH of 11-12, possesses strong alkaline properties.
- Sodium Hydroxide (Lye): This highly corrosive chemical, with a pH of 13-14, is used in various industrial applications.
- Liquid Drain Cleaner: These potent solutions, with a pH of 12-14, effectively dissolve clogs in drains.
The Importance of pH in Everyday Life:
The pH scale plays a crucial role in various aspects of our lives, influencing the following:
- Human Health: Maintaining the pH balance of our blood, stomach, and skin is essential for overall well-being. Deviations from the optimal pH can lead to various health issues.
- Agriculture: Soil pH significantly impacts plant growth and nutrient availability. Understanding and adjusting soil pH is crucial for successful crop production.
- Food Preservation: The pH of food influences its susceptibility to spoilage. Acidic environments inhibit bacterial growth, contributing to longer shelf life.
- Environmental Protection: Monitoring pH levels in water bodies is crucial for assessing water quality and protecting aquatic ecosystems.
- Industrial Applications: Various industries rely on pH control for optimal product performance, safety, and efficiency.
FAQs About the pH Scale:
1. How is pH measured?
pH is typically measured using a pH meter, a device equipped with a pH-sensitive electrode. Alternatively, pH indicator solutions or pH paper strips can provide a qualitative assessment of acidity or alkalinity.
2. What are the benefits of knowing the pH of a substance?
Knowing the pH of a substance allows us to predict its chemical properties, potential interactions with other substances, and its suitability for specific applications.
3. What are the risks associated with highly acidic or alkaline substances?
Highly acidic or alkaline substances can be corrosive and cause skin burns, eye irritation, and other health problems. It’s essential to handle them with caution and appropriate protective gear.
4. How can I maintain the pH balance in my body?
Maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and managing stress can contribute to a healthy pH balance in the body.
5. Can pH be changed?
Yes, pH can be altered by adding acids or bases to a solution. For example, adding lemon juice (acidic) to water lowers its pH, while adding baking soda (alkaline) raises its pH.
Tips for Understanding and Using the pH Scale:
- Pay attention to pH labels: Many products, including household cleaners, food items, and personal care products, list their pH values on their labels.
- Use pH test strips: These convenient strips can quickly assess the pH of various solutions, providing a visual indication of their acidity or alkalinity.
- Be cautious with strong acids and bases: Always wear appropriate safety gear when handling these substances and store them in well-ventilated areas.
- Consult a professional: If you’re unsure about the pH of a substance or its potential effects, consult a chemist or other qualified professional.
Conclusion: The pH Scale: A Powerful Tool for Understanding Our World
The pH scale provides a powerful framework for understanding the acidic or alkaline nature of substances, revealing the intricate balance that governs various aspects of our world. From the delicate chemistry of our bodies to the diverse ecosystems around us, the pH scale plays a vital role in maintaining harmony and ensuring the proper functioning of our planet. By appreciating its significance and using it wisely, we can navigate the complexities of our world with a deeper understanding of the forces that shape it.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of the pH Scale: A Journey Through Everyday Acidity and Alkalinity. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!