Unveiling the Nature of Alpha Particles: A Journey into the Heart of Radioactive Decay
Related Articles: Unveiling the Nature of Alpha Particles: A Journey into the Heart of Radioactive Decay
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Nature of Alpha Particles: A Journey into the Heart of Radioactive Decay. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Nature of Alpha Particles: A Journey into the Heart of Radioactive Decay
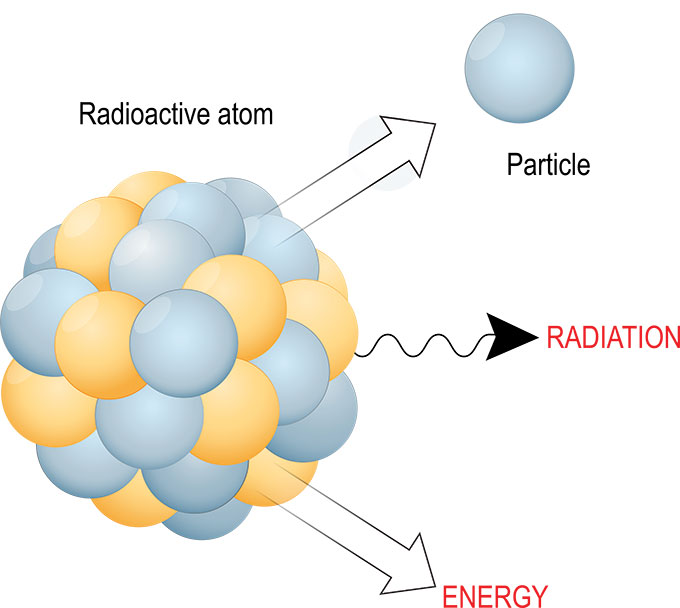
Alpha particles, often denoted as α particles, are a fascinating aspect of nuclear physics, representing a fundamental component of radioactive decay. These particles, comprising two protons and two neutrons tightly bound together, are essentially helium nuclei stripped of their electrons. This inherent structure imbues them with unique properties that have profound implications in various scientific fields, from nuclear energy to medical applications.
Understanding the Essence of Alpha Particles
The discovery of alpha particles can be traced back to the pioneering work of Ernest Rutherford in the early 20th century. While investigating the nature of radioactivity, Rutherford observed that certain materials emitted highly energetic particles that could penetrate thin sheets of metal. He labeled these particles as alpha particles, realizing their distinct nature from other radioactive emissions like beta particles and gamma rays.
Alpha particles are characterized by their relatively large mass and positive charge, stemming from the presence of two protons. This inherent structure leads to a number of defining properties:
- High Ionizing Power: Due to their large mass and charge, alpha particles interact strongly with matter, readily stripping electrons from atoms along their path. This ionization process results in the creation of ions, leading to significant damage to biological tissues.
- Short Range: Despite their high energy, alpha particles have a limited range in matter. Their large size and strong interactions with electrons cause them to lose energy rapidly, resulting in a short path length, typically measured in centimeters in air. This limited range makes them relatively harmless outside the body, as they are easily absorbed by the skin and cannot penetrate deeply.
- High Energy: Alpha particles are emitted with substantial kinetic energy, typically in the range of several mega-electron volts (MeV). This high energy is a consequence of the strong nuclear forces binding the protons and neutrons within the alpha particle.
The Role of Alpha Particles in Radioactive Decay
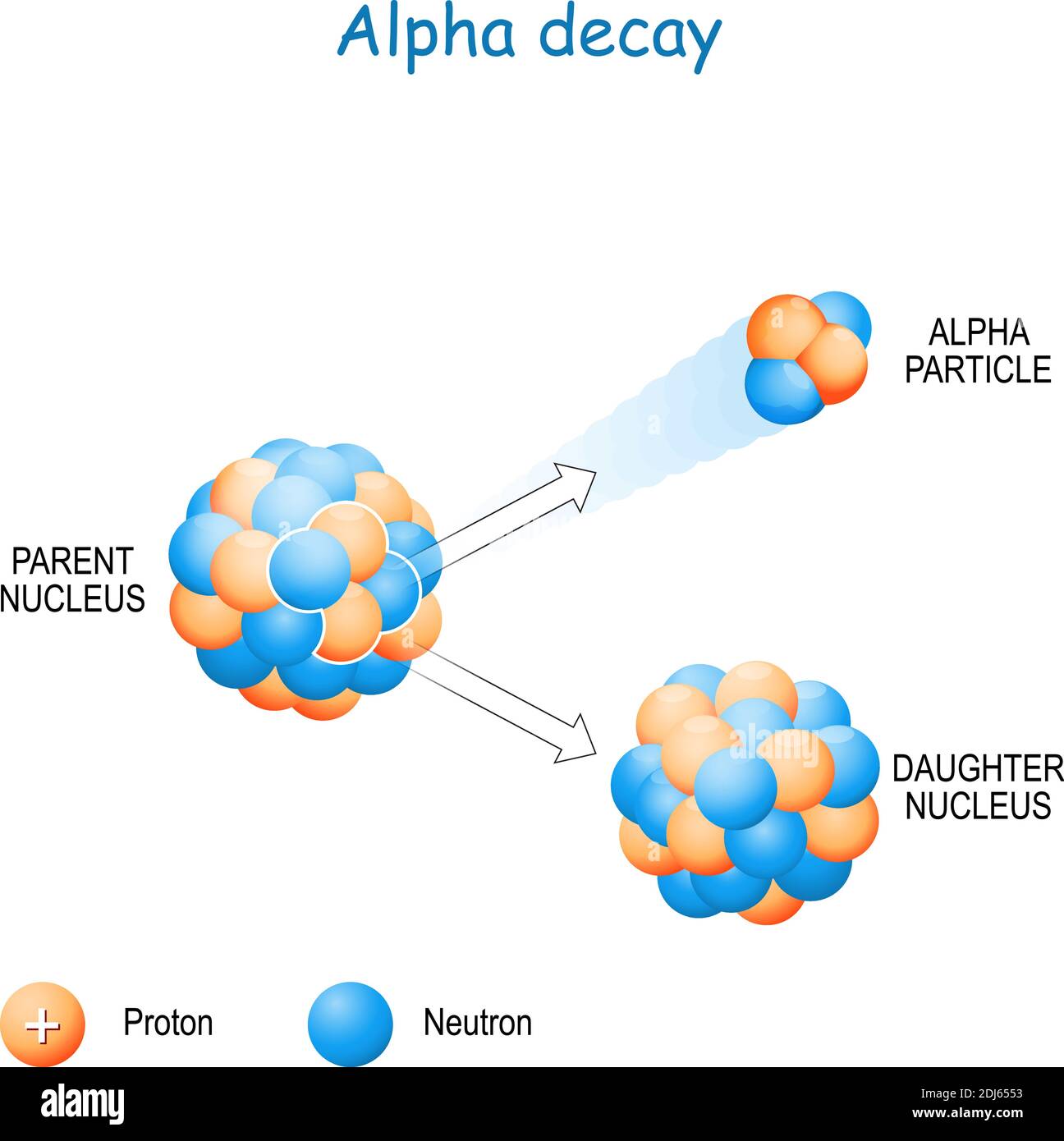
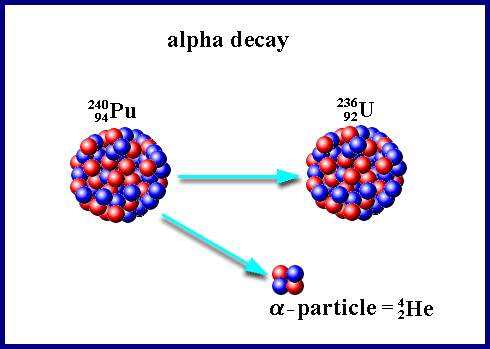
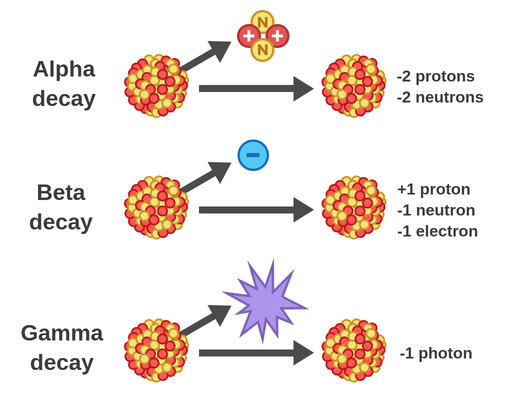
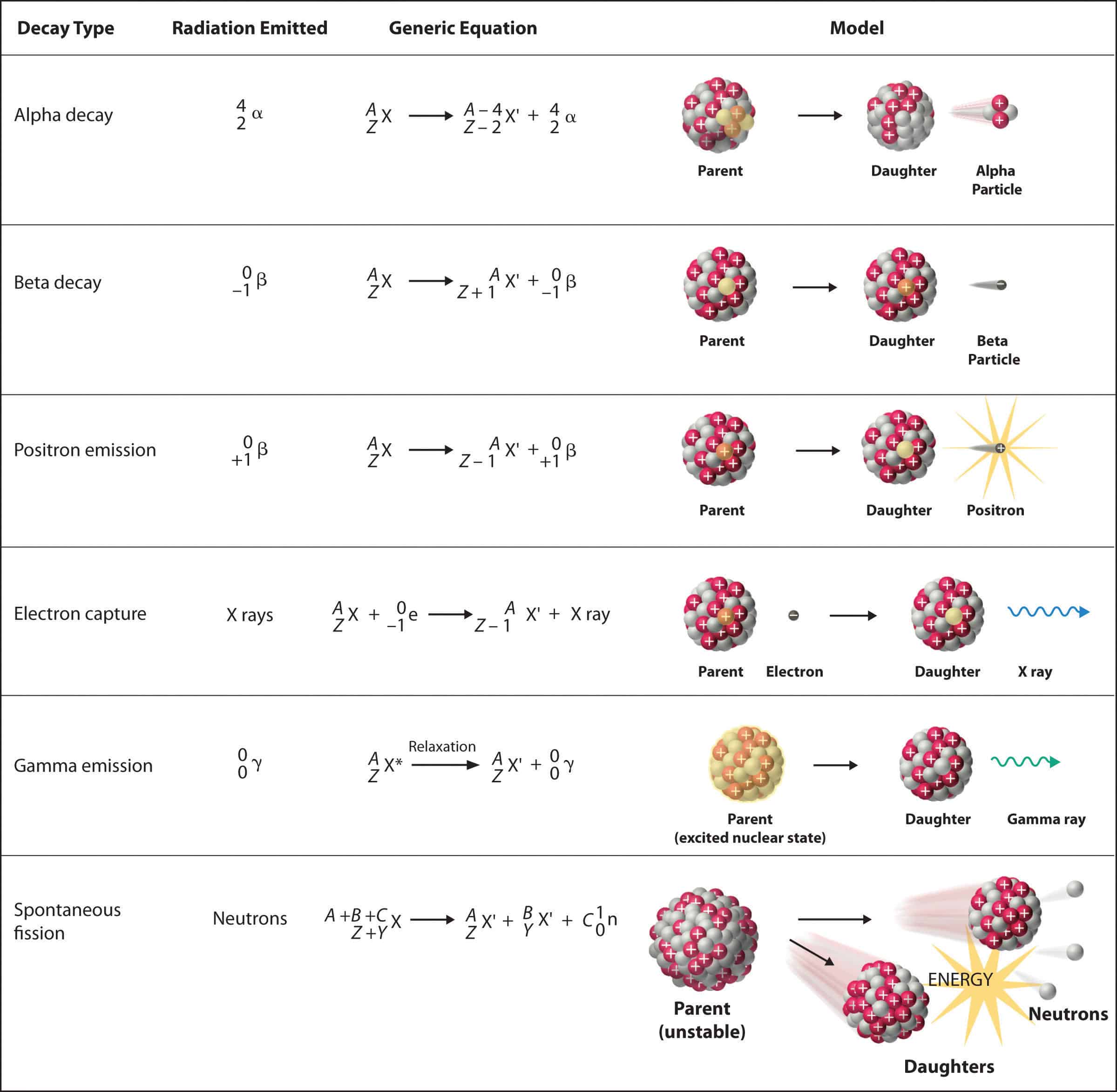
Alpha decay is a fundamental process in nuclear physics, where an unstable atomic nucleus releases an alpha particle, transforming into a different element with a lower atomic number. This process is governed by the principle of achieving greater stability, as the daughter nucleus resulting from the decay often has a lower energy state compared to the parent nucleus.
The process of alpha decay can be represented by the following equation:
Parent Nucleus → Daughter Nucleus + Alpha Particle
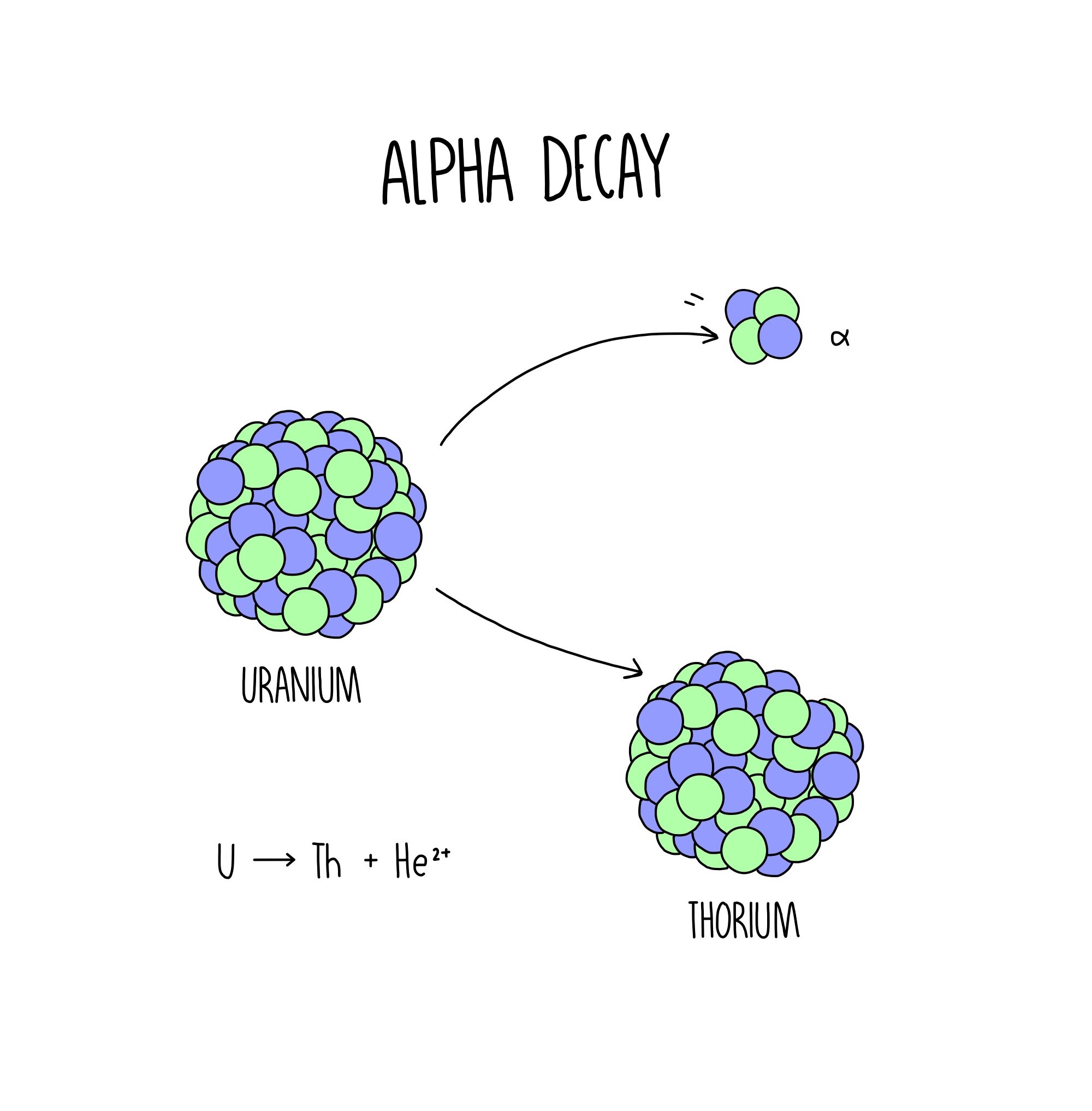
For instance, the radioactive decay of uranium-238 (U-238) into thorium-234 (Th-234) involves the emission of an alpha particle:
U-238 → Th-234 + α
This equation demonstrates the change in atomic number (Z) and mass number (A) during alpha decay. The parent nucleus loses two protons (Z decreases by 2) and four nucleons (A decreases by 4) due to the emission of the alpha particle.
Applications of Alpha Particles
Alpha particles, despite their inherent danger due to their ionizing power, find applications in various fields, primarily due to their high energy and unique properties:
- Smoke Detectors: Alpha particles are used in ionization smoke detectors, where their ionizing ability is utilized to create a small electric current. When smoke particles enter the detector, they interfere with the current flow, triggering the alarm.
- Medical Imaging and Therapy: Alpha particles are increasingly employed in medical imaging and therapy, particularly in targeted alpha therapy (TAT). TAT uses alpha-emitting isotopes attached to antibodies or other molecules that specifically target cancer cells. This approach allows for highly localized radiation delivery, maximizing cancer cell destruction while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
- Nuclear Energy: Alpha decay is a crucial process in nuclear reactors, where it contributes to the energy release through the fission of uranium. Alpha particles also play a role in the production of plutonium, a key component in nuclear weapons.
- Scientific Research: Alpha particles are valuable tools in various scientific research fields. They are used in scattering experiments to study the structure of atomic nuclei and in the development of new materials with improved properties.
FAQs about Alpha Particles
1. Are Alpha Particles Harmful to Humans?
Yes, alpha particles are harmful to humans, especially when inhaled or ingested. Their high ionizing power can cause significant damage to DNA and cells, leading to various health issues, including cancer. However, their short range in matter makes them less dangerous outside the body, as they are easily absorbed by the skin and cannot penetrate deeply.
2. How Can Alpha Particles Be Detected?
Alpha particles can be detected using various methods, including:
- Scintillation Counters: These detectors utilize materials that emit light when struck by an alpha particle, allowing for the detection and quantification of the particles.
- Cloud Chambers: This device uses supersaturated vapor to visualize the tracks of alpha particles as they ionize the air molecules.
- Nuclear Track Detectors: These detectors use solid materials that are sensitive to alpha particles, creating tracks that can be observed and analyzed.
3. What is the Difference Between Alpha Particles and Beta Particles?
Alpha particles and beta particles are both emitted during radioactive decay, but they differ significantly in their composition and properties:
- Alpha Particles: Consist of two protons and two neutrons, carrying a +2 charge and having a relatively large mass.
- Beta Particles: Are high-energy electrons or positrons, carrying a -1 or +1 charge, respectively, and having a much smaller mass than alpha particles.
4. What is the Role of Alpha Particles in the Sun?
Alpha particles play a crucial role in the nuclear fusion reactions occurring within the Sun. In the core of the Sun, hydrogen nuclei (protons) fuse together to form helium nuclei (alpha particles), releasing enormous amounts of energy in the process. This energy is responsible for the Sun’s luminosity and heat.
5. How Do Alpha Particles Contribute to Radiation Therapy?
Alpha particles are increasingly used in radiation therapy, particularly in targeted alpha therapy (TAT). This approach utilizes alpha-emitting isotopes attached to molecules that specifically target cancer cells. The high ionizing power of alpha particles effectively destroys cancer cells while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
Tips for Understanding Alpha Particles
- Visualize the Structure: Imagine an alpha particle as a tiny, tightly bound package of two protons and two neutrons, resembling a miniature helium nucleus.
- Focus on the Properties: Remember the key properties of alpha particles: high ionizing power, short range, and high energy.
- Relate to Everyday Examples: Think of smoke detectors, where alpha particles are used to detect smoke, or medical imaging techniques that employ alpha particles for diagnostic purposes.
- Explore the Applications: Understand how alpha particles are used in various fields, from nuclear energy to medical therapy and scientific research.
Conclusion
Alpha particles, despite their inherent danger due to their ionizing power, represent a fascinating and important aspect of nuclear physics. Their unique properties, including high energy, short range, and high ionizing power, have led to a wide range of applications in various fields, from smoke detection to medical therapy and scientific research. As our understanding of these particles continues to grow, their potential for innovation and advancement in various scientific disciplines remains immense.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Nature of Alpha Particles: A Journey into the Heart of Radioactive Decay. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!