Understanding the Dynamics of Supply: A Comprehensive Look at Supply Shifters
Related Articles: Understanding the Dynamics of Supply: A Comprehensive Look at Supply Shifters
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Dynamics of Supply: A Comprehensive Look at Supply Shifters. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Dynamics of Supply: A Comprehensive Look at Supply Shifters

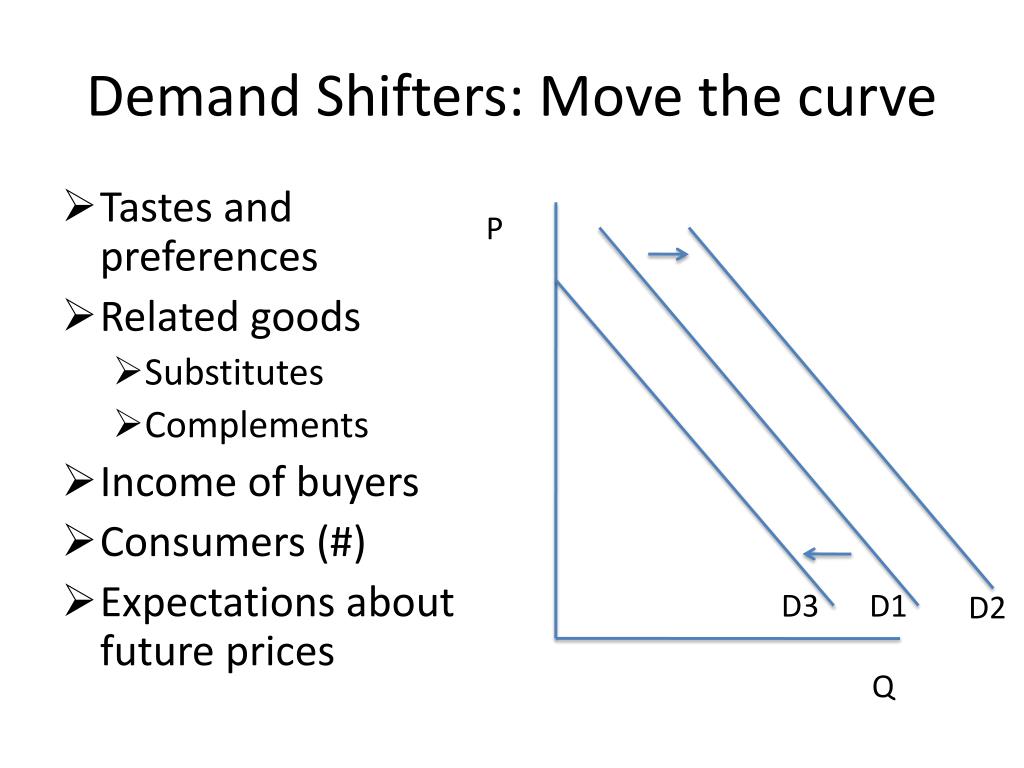
In the realm of economics, understanding the interplay between supply and demand is crucial for comprehending market dynamics. While demand represents the consumer’s desire for a product or service, supply refers to the quantity of goods or services producers are willing and able to offer at various prices. This article delves into the concept of supply shifters, factors that influence the supply curve, and how they impact market equilibrium.
Supply Curve: A Visual Representation of Supply
The supply curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity supplied. Typically, the curve slopes upwards, indicating that as the price increases, producers are willing to offer more of the product. This positive relationship stems from the principle of profit maximization: higher prices incentivize producers to increase production to earn greater profits.
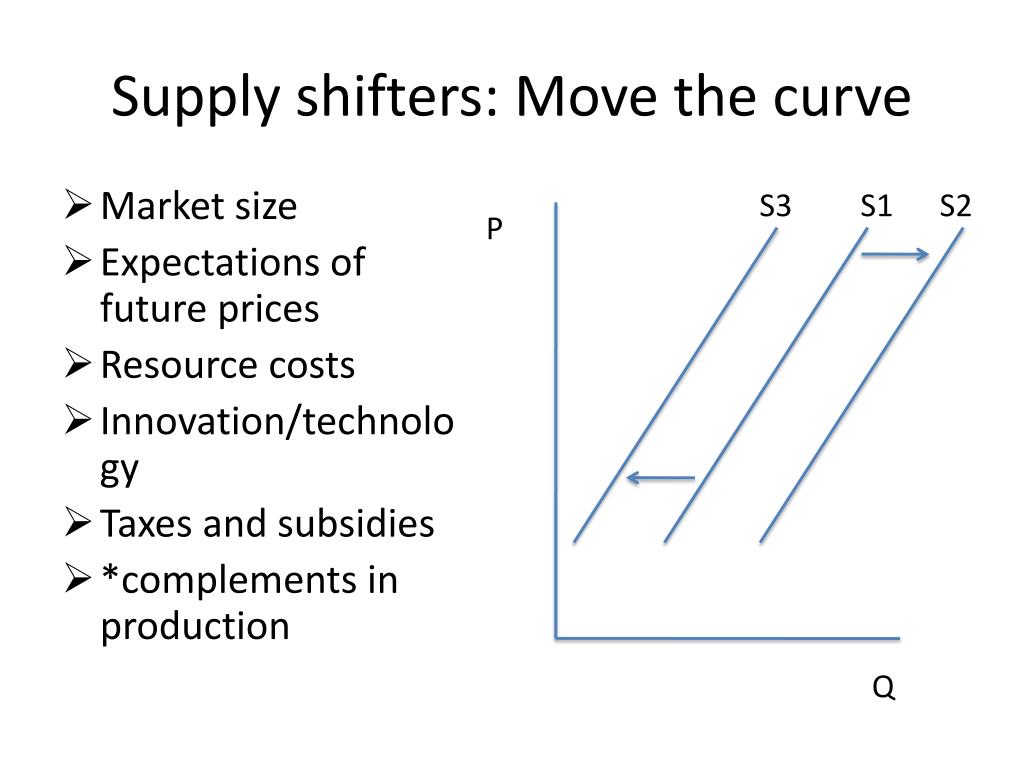
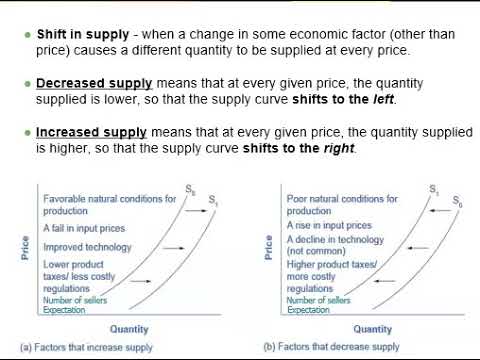
Factors Shifting the Supply Curve: The Determinants of Supply
While changes in price cause movement along the supply curve, certain factors can shift the entire curve itself. These factors are known as supply shifters. Understanding these factors is essential for predicting and analyzing market behavior.
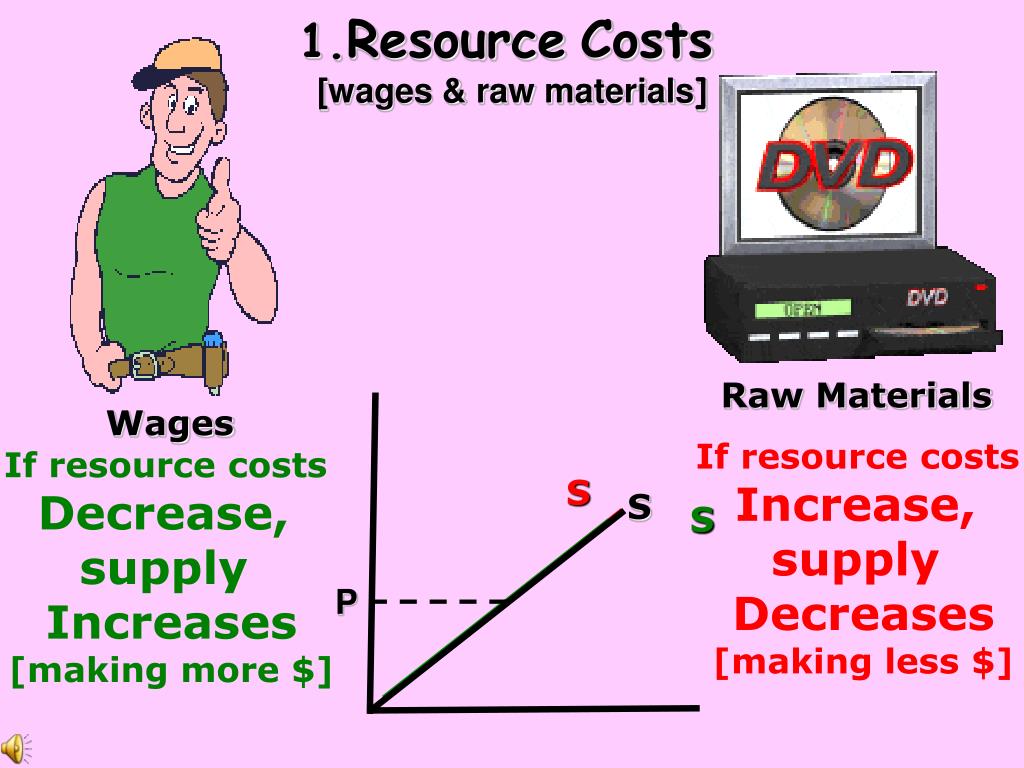
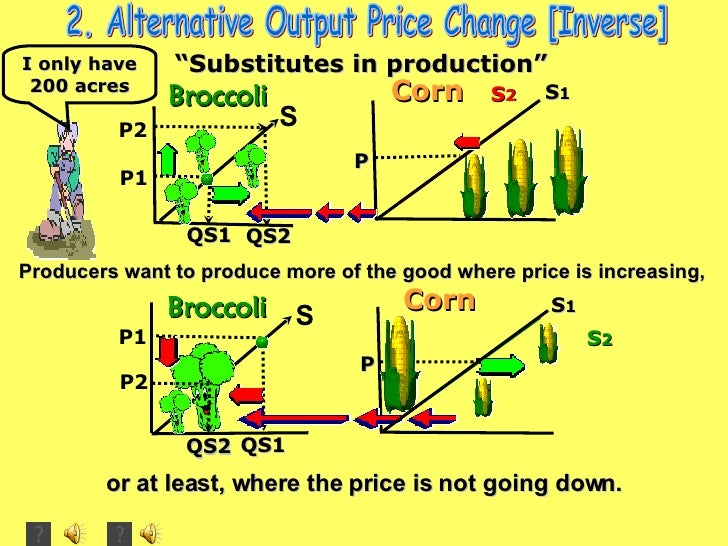
1. Input Prices:
- Definition: Input prices refer to the cost of resources used in production, such as raw materials, labor, energy, and capital.
- Impact: A decrease in input prices reduces production costs, making it more profitable for producers to supply a larger quantity at each price level. Consequently, the supply curve shifts to the right. Conversely, an increase in input prices increases production costs, leading to a leftward shift in the supply curve.
- Example: Consider the production of coffee. A decline in the price of coffee beans (a key input) would lower production costs for coffee producers, encouraging them to supply more coffee at each price level. This would shift the supply curve for coffee to the right.
2. Technology:
- Definition: Technological advancements can enhance production efficiency, allowing producers to produce more output with the same or fewer resources.
- Impact: Improved technology typically leads to a rightward shift in the supply curve. As producers can produce more efficiently, they are willing to supply a larger quantity at each price level.
- Example: The introduction of automated assembly lines in the automotive industry has significantly increased production efficiency, enabling car manufacturers to produce more vehicles at lower costs. This technological advancement has shifted the supply curve for automobiles to the right.
3. Number of Sellers:
- Definition: The number of producers in a market can significantly impact supply.
- Impact: An increase in the number of sellers leads to a rightward shift in the supply curve. With more producers entering the market, the overall quantity supplied at each price level increases. Conversely, a decrease in the number of sellers leads to a leftward shift in the supply curve.
- Example: The rise of online marketplaces like Etsy has increased the number of sellers for handcrafted goods, leading to a rightward shift in the supply curve for these products.
4. Government Regulations:
- Definition: Government policies, such as taxes, subsidies, and regulations, can influence production costs and incentives for producers.
- Impact: Regulations that increase production costs, such as environmental regulations or stricter safety standards, typically lead to a leftward shift in the supply curve. Conversely, subsidies or tax breaks designed to incentivize production can shift the supply curve to the right.
- Example: The imposition of stricter environmental regulations on the manufacturing industry could increase production costs for firms, leading to a decrease in supply and a leftward shift in the supply curve.
5. Expectations:
- Definition: Producers’ expectations about future market conditions, such as anticipated price changes or demand fluctuations, can influence their current supply decisions.
- Impact: If producers anticipate higher prices in the future, they may choose to reduce current supply to sell more at the higher prices later. This would result in a leftward shift in the supply curve. Conversely, if producers expect lower prices in the future, they may increase current supply to take advantage of current market conditions, shifting the supply curve to the right.
- Example: If a manufacturer expects the price of steel to rise in the coming months, they might choose to reduce their current steel production to sell more at the higher prices later. This would shift the supply curve for steel to the left.
6. Natural Disasters and Other Events:
- Definition: Natural disasters, such as floods, earthquakes, or droughts, can disrupt production processes and affect the availability of resources, impacting supply.
- Impact: Natural disasters typically lead to a leftward shift in the supply curve. The destruction of infrastructure, crops, or other essential resources can significantly reduce production capacity.
- Example: A severe drought could significantly reduce the supply of agricultural products, shifting the supply curve for those products to the left.
Understanding the Impact of Supply Shifters on Market Equilibrium
The interaction of supply and demand determines the equilibrium price and quantity in a market. Supply shifters play a crucial role in influencing this equilibrium.
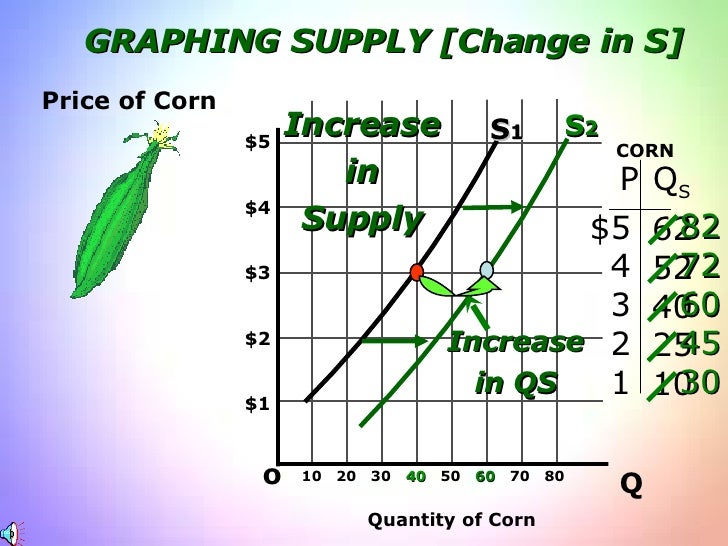
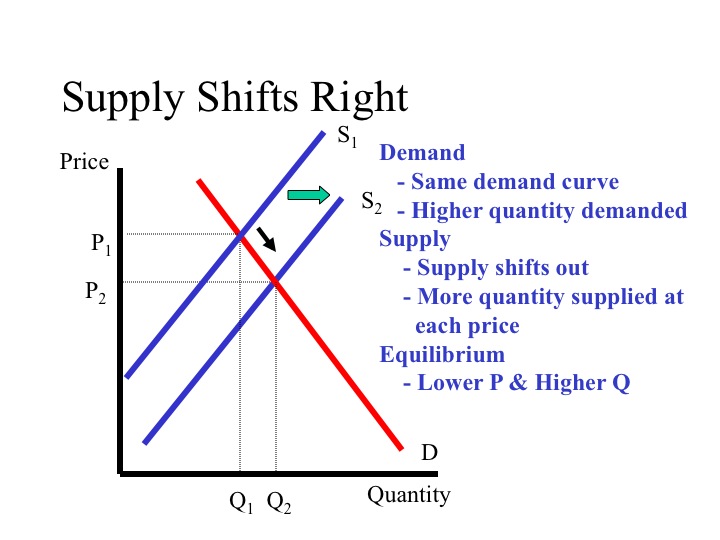
- Rightward Shift in Supply: When the supply curve shifts to the right, the equilibrium price decreases, and the equilibrium quantity increases. This occurs because producers are now willing to supply more at each price level, leading to lower prices and higher quantities demanded.
- Leftward Shift in Supply: Conversely, a leftward shift in the supply curve leads to an increase in the equilibrium price and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity. This is because producers are now supplying less at each price level, resulting in higher prices and lower quantities demanded.
Examples of Supply Shifters in Action
1. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Supply of Medical Supplies:
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted the supply of essential medical supplies, such as masks, ventilators, and personal protective equipment (PPE). The increased demand for these products, coupled with disruptions in supply chains and production facilities, led to a leftward shift in the supply curve. This resulted in a shortage of medical supplies, driving up prices and creating challenges for healthcare systems worldwide.
2. The Effect of Technological Advancements on the Supply of Solar Panels:
Technological advancements in solar panel production have significantly reduced the cost of producing solar energy. This has led to a rightward shift in the supply curve for solar panels, making them more affordable and accessible to consumers. The increased supply has also driven down prices, making solar energy a more competitive alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
3. The Influence of Government Regulations on the Supply of Gasoline:
Government regulations, such as fuel efficiency standards and environmental regulations, can influence the supply of gasoline. For example, stricter fuel efficiency standards for automobiles can reduce demand for gasoline, potentially leading to a leftward shift in the supply curve. Conversely, subsidies for renewable energy sources could incentivize the production of alternative fuels, leading to a rightward shift in the supply curve for gasoline.
FAQs on Supply Shifters
1. What is the difference between a change in supply and a change in quantity supplied?
A change in supply refers to a shift in the entire supply curve, caused by a change in one of the supply shifters discussed earlier. A change in quantity supplied refers to a movement along the existing supply curve, caused solely by a change in price.
2. Can supply shifters affect demand?
While supply shifters primarily affect the supply curve, they can indirectly influence demand. For example, a decrease in the supply of a product due to a natural disaster can lead to higher prices, which in turn could reduce demand for the product.
3. How can I use supply shifters to make better business decisions?
By understanding the factors that can shift the supply curve, businesses can make informed decisions about pricing, production levels, and resource allocation. For example, a business might anticipate a decrease in input prices and adjust its production plans accordingly.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing Supply Shifters
- Stay informed: Keep abreast of industry trends, technological advancements, and government policies that could impact your business or industry.
- Analyze your costs: Regularly review your input costs and identify opportunities to reduce them through sourcing, negotiation, or technological improvements.
- Monitor competitors: Analyze the actions of your competitors and consider how their decisions might affect the supply curve in your industry.
- Be proactive: Anticipate potential supply disruptions and develop contingency plans to mitigate their impact.
Conclusion
Supply shifters are fundamental drivers of market dynamics. By understanding these factors and their impact on the supply curve, we can gain valuable insights into how markets function and make informed decisions in a variety of contexts. From business strategy to policy analysis, comprehending the influence of supply shifters is essential for navigating the complexities of the economic landscape.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Dynamics of Supply: A Comprehensive Look at Supply Shifters. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!