The Spectrum of Light: Exploring the World of Electromagnetic Waves
Related Articles: The Spectrum of Light: Exploring the World of Electromagnetic Waves
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Spectrum of Light: Exploring the World of Electromagnetic Waves. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Spectrum of Light: Exploring the World of Electromagnetic Waves
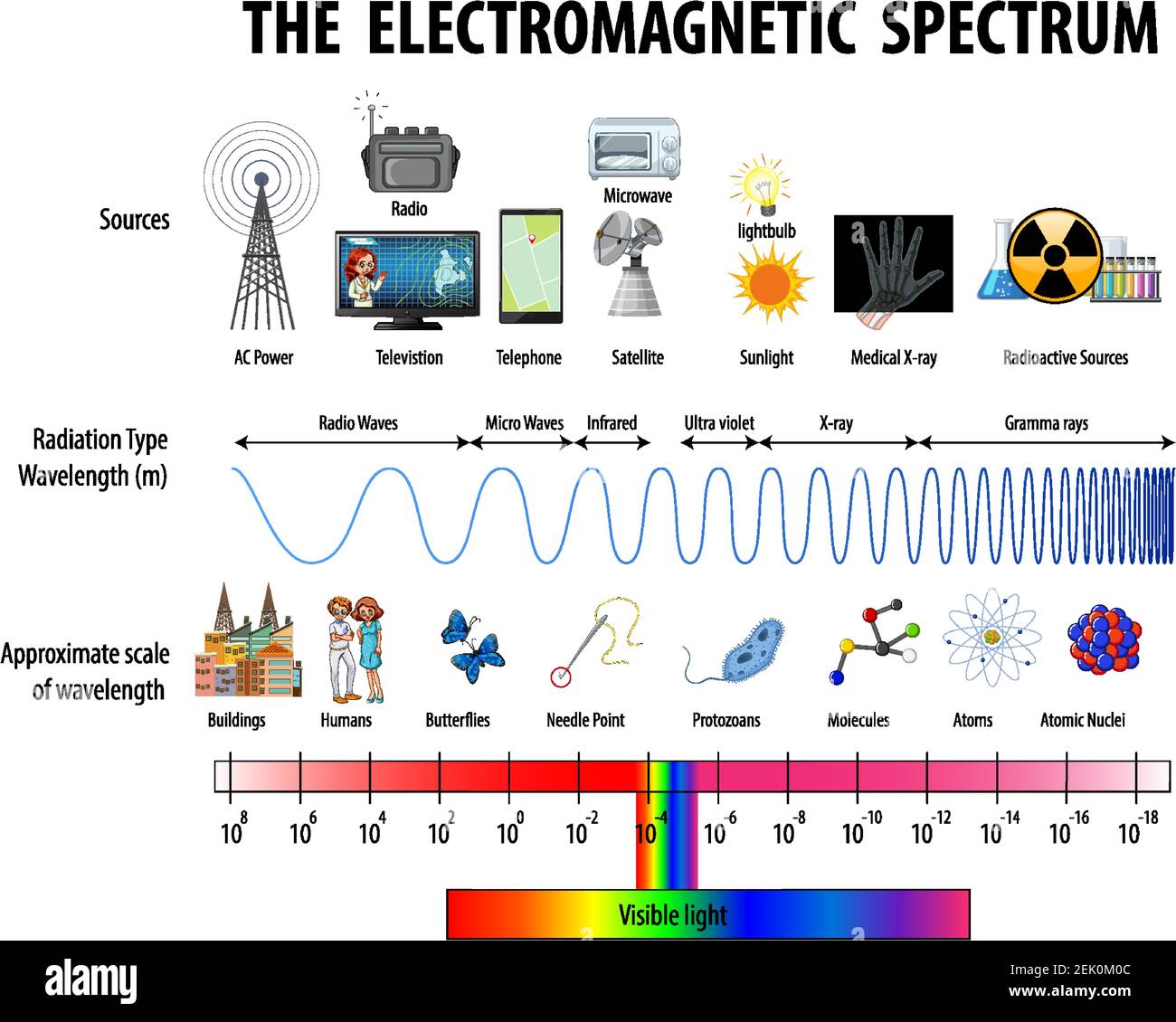
The universe is awash in a sea of invisible energy, constantly pulsing and vibrating. This energy, known as electromagnetic radiation, manifests itself in a vast spectrum of waves, each with unique properties and applications. From the warmth of the sun to the images we see on our screens, electromagnetic waves play a crucial role in our understanding and interaction with the world.
Understanding the Fundamentals:
Electromagnetic waves are a fascinating combination of electric and magnetic fields, oscillating perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation. These waves travel at the speed of light, a constant value in a vacuum, and exhibit wave-like characteristics such as wavelength and frequency. The relationship between these two properties is inversely proportional, meaning as the wavelength decreases, the frequency increases.
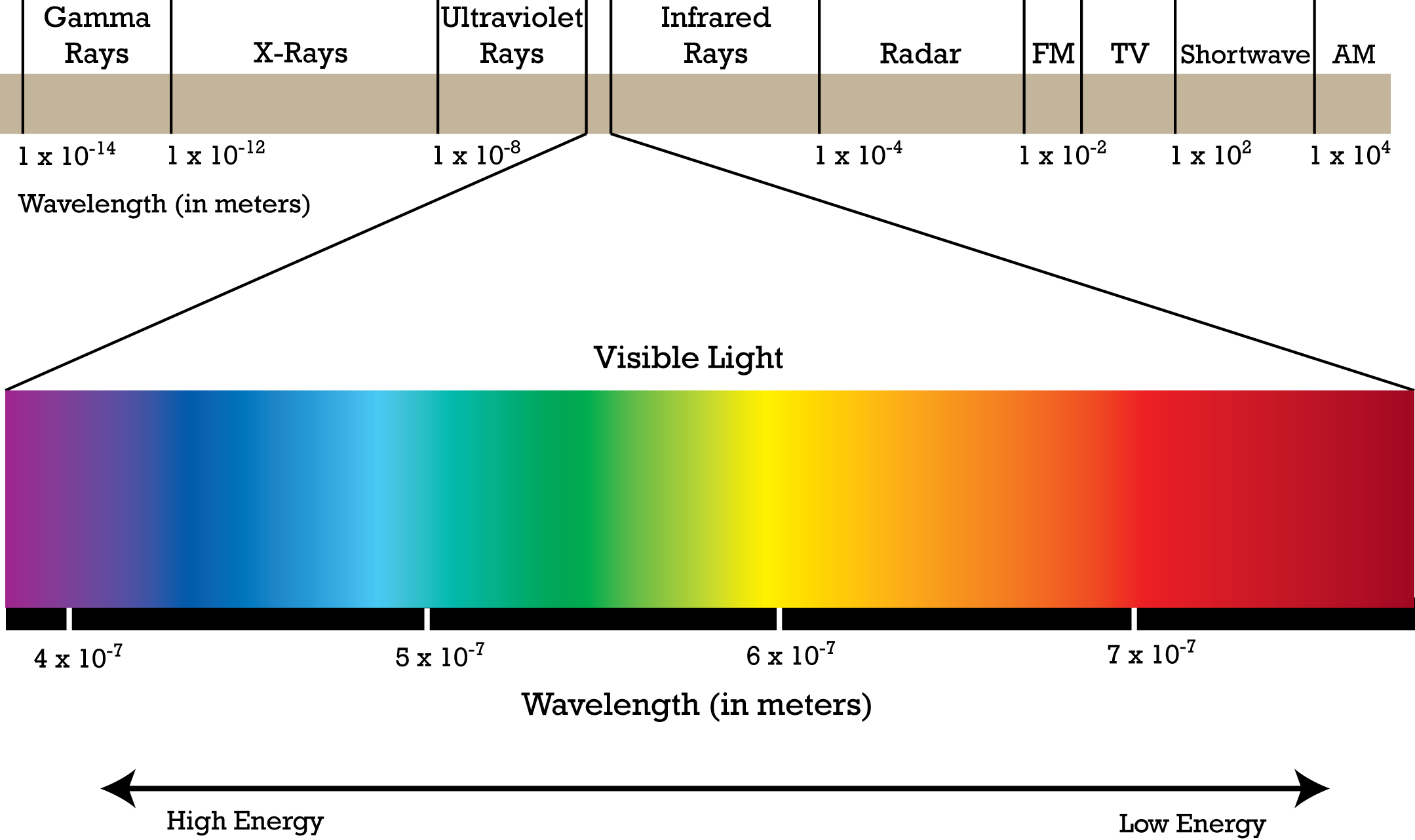
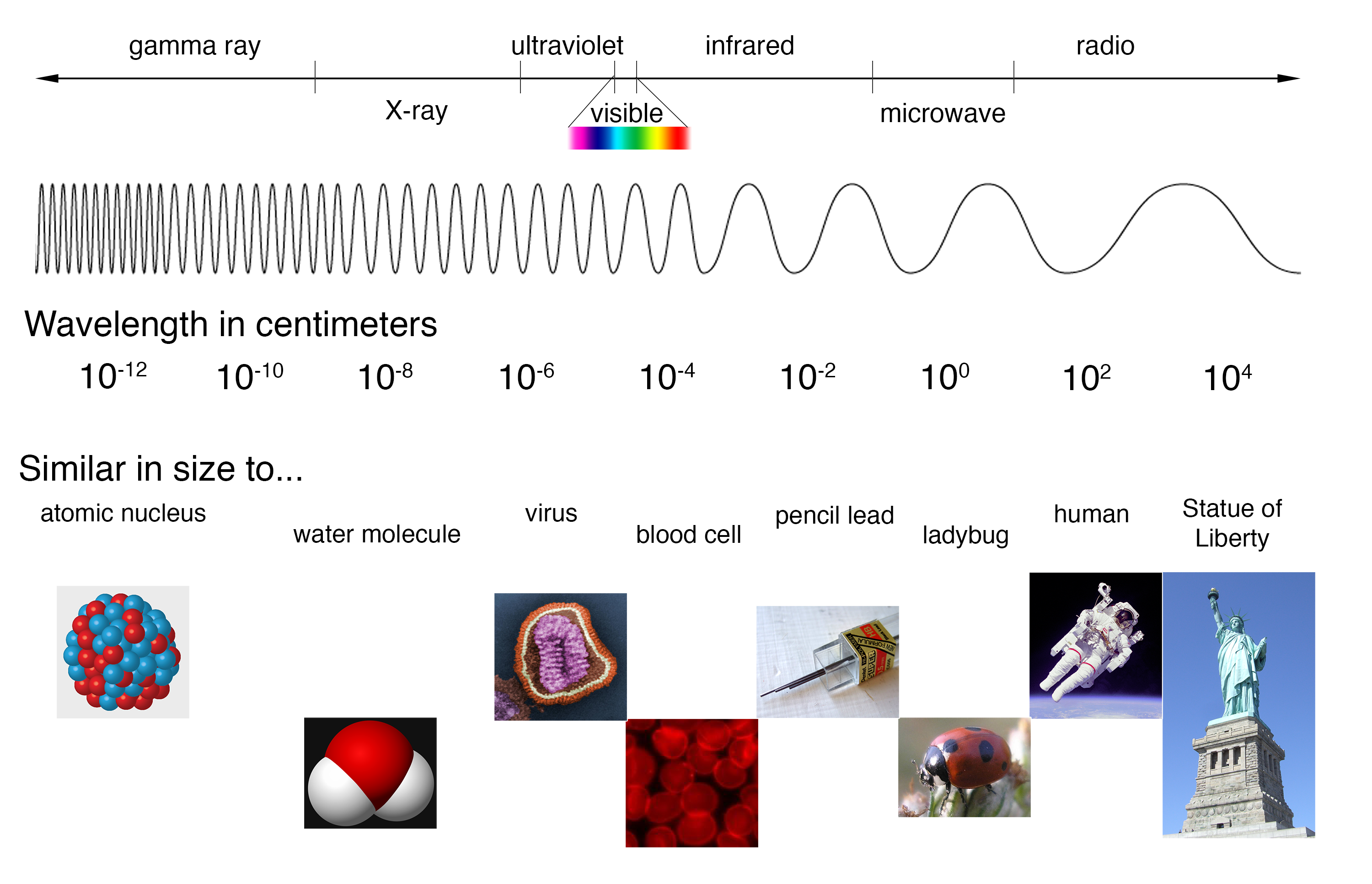
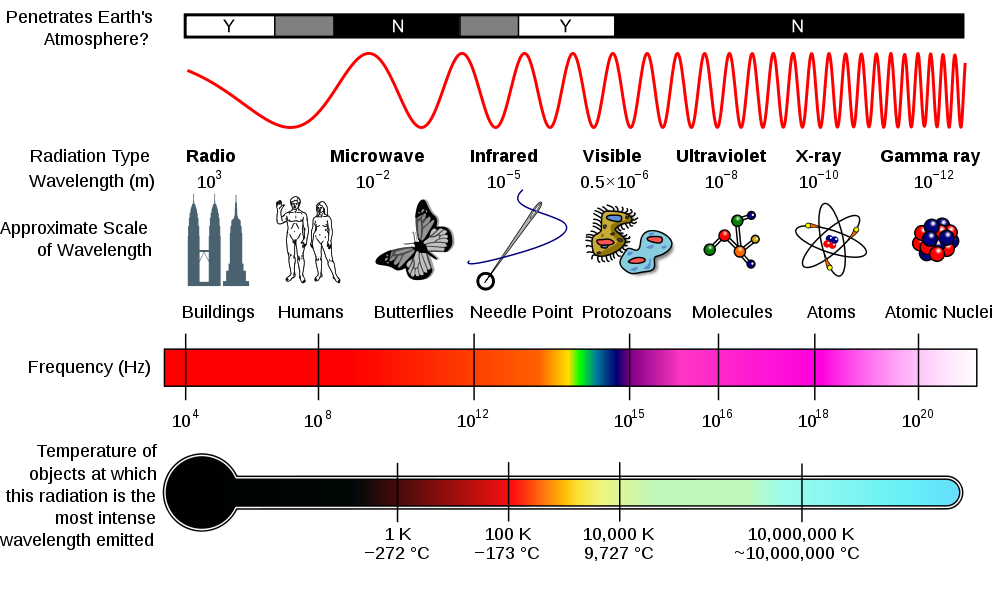
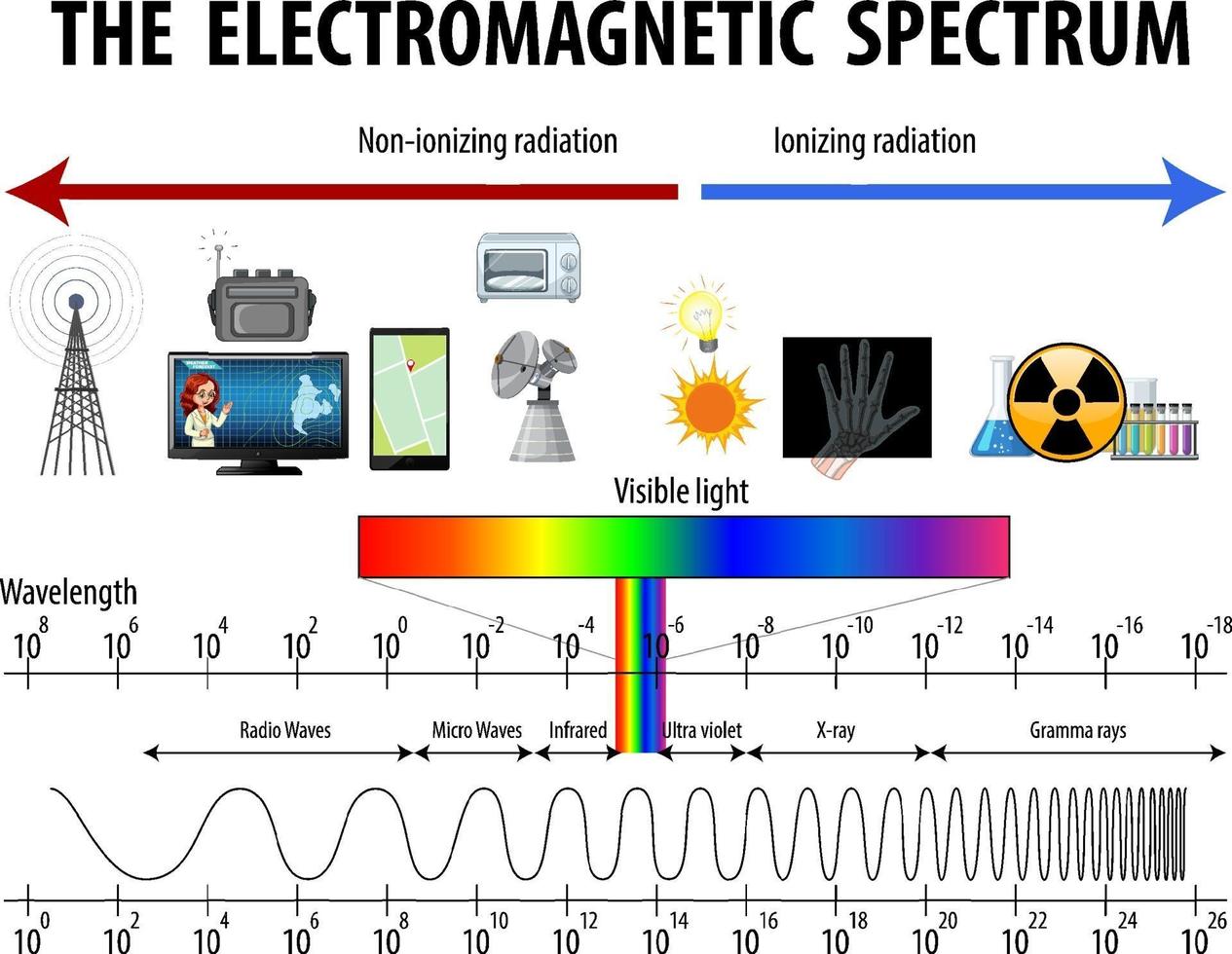
This intricate dance of electric and magnetic fields gives rise to the diverse spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, ranging from the low-frequency radio waves to the high-frequency gamma rays. Each region of this spectrum possesses distinct properties and applications, shaping our technological advancements and our understanding of the universe.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Journey Through the Waves
-
Radio Waves: These long-wavelength waves, typically spanning from millimeters to kilometers, are the workhorses of communication. They carry radio broadcasts, television signals, and data across vast distances. Their low energy levels make them ideal for transmitting information through the atmosphere and even bouncing off the ionosphere, enabling global communication.
- Example: AM and FM radio broadcasts rely on radio waves to transmit audio signals.
- Benefit: Enables long-distance communication, vital for broadcasting, navigation, and satellite communication.
-
Microwaves: Occupying the spectrum between radio waves and infrared radiation, microwaves are known for their ability to heat objects. Their shorter wavelengths allow them to penetrate food and generate heat through molecular agitation. They also play a crucial role in communication, facilitating high-speed data transfer in wireless networks and satellite communication.
- Example: Microwave ovens utilize microwaves to heat food quickly and efficiently.
- Benefit: Enables efficient heating, high-speed communication, and weather monitoring through radar technology.
-
Infrared Radiation: Invisible to the human eye, infrared radiation is the heat we feel from the sun or a warm object. It plays a vital role in thermal imaging, allowing us to detect heat signatures and visualize objects in the dark. It also finds applications in medical diagnostics and remote sensing.
- Example: Infrared cameras are used in security systems to detect intruders and in medical imaging to diagnose injuries and monitor blood flow.
- Benefit: Enables night vision, thermal imaging, and medical diagnostics.
-
Visible Light: This narrow band of the electromagnetic spectrum is the only portion visible to the human eye, encompassing the colors of the rainbow. Our perception of color is determined by the wavelength of light reflected from objects. Visible light is essential for vision and plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
- Example: Sunlight enables us to see the world around us and is essential for plant life.
- Benefit: Enables vision, photosynthesis, and artistic expression through painting and photography.
-
Ultraviolet Radiation: Invisible to the human eye, ultraviolet radiation carries more energy than visible light. It is responsible for sunburns and tanning, but it also plays a role in vitamin D production in the skin. Ultraviolet radiation is used in sterilization, medical treatments, and forensic investigations.
- Example: UV light is used to sterilize medical instruments and purify water.
- Benefit: Enables sterilization, medical treatment, and forensic analysis.
-
X-Rays: Penetrating radiation with high energy, X-rays can pass through soft tissues but are absorbed by denser materials like bones. This property makes them invaluable for medical imaging, allowing doctors to visualize the internal structure of the body. X-rays also find applications in security screening and material analysis.
- Example: X-ray imaging is used to diagnose fractures, detect tumors, and screen luggage at airports.
- Benefit: Enables medical imaging, security screening, and material analysis.
-
Gamma Rays: The most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation, gamma rays are emitted from radioactive decay and nuclear reactions. They possess the highest penetrating power and can be used in radiation therapy to treat cancer and in sterilization techniques.
- Example: Gamma rays are used in cancer treatment and sterilization of medical equipment.
- Benefit: Enables cancer treatment, sterilization, and nuclear research.
FAQs about Electromagnetic Waves:
1. How are electromagnetic waves generated?
Electromagnetic waves are generated by the acceleration of charged particles. For example, radio waves are generated by the movement of electrons in an antenna, while X-rays are produced by the rapid deceleration of electrons.
2. What is the relationship between frequency and energy of electromagnetic waves?
The energy of an electromagnetic wave is directly proportional to its frequency. This means that higher frequency waves, like gamma rays, carry more energy than lower frequency waves, like radio waves.
3. How do electromagnetic waves travel through space?
Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium to travel. They can propagate through the vacuum of space, as well as through matter.
4. What are the dangers of electromagnetic radiation?
While electromagnetic radiation is essential for many applications, exposure to high levels of certain types of radiation can be harmful. For example, excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation can cause skin cancer, and exposure to high doses of X-rays or gamma rays can cause radiation sickness.
5. How are electromagnetic waves used in technology?
Electromagnetic waves are used in countless technological applications, including communication, medical imaging, heating, security, and scientific research.
Tips for Understanding Electromagnetic Waves:
- Visualize the spectrum: Imagine the electromagnetic spectrum as a continuous rainbow, with radio waves at one end and gamma rays at the other.
- Think about wavelength and frequency: Remember that wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional, meaning shorter wavelengths correspond to higher frequencies.
- Connect applications to properties: Try to understand how the properties of each type of electromagnetic wave relate to its applications.
- Explore the world around you: Look for examples of electromagnetic radiation in everyday life, from the light from your phone screen to the heat from a stovetop.
Conclusion:
Electromagnetic waves are a fundamental aspect of our universe, shaping our understanding of the cosmos and driving technological innovation. From the communication signals that connect us to the world to the medical tools that diagnose and treat diseases, these invisible waves play a vital role in our daily lives. By understanding their properties and applications, we can harness the power of electromagnetic radiation to advance our knowledge and improve our world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Spectrum of Light: Exploring the World of Electromagnetic Waves. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!