The Silent Language of Safety: Deciphering Hazard Symbols
Related Articles: The Silent Language of Safety: Deciphering Hazard Symbols
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Silent Language of Safety: Deciphering Hazard Symbols. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Silent Language of Safety: Deciphering Hazard Symbols

Hazard symbols are a universal language of safety, conveying critical information about potential risks in a concise and easily understandable manner. These symbols, often depicted in the form of pictograms, play a vital role in safeguarding individuals and the environment by providing clear warnings and instructions.
Understanding the Significance of Hazard Symbols
Hazard symbols are not merely decorative elements. They serve as powerful tools for communication, facilitating the quick identification and comprehension of potential dangers. Their significance lies in their ability to:
- Promote Safety Awareness: By visually highlighting potential hazards, these symbols enhance awareness and encourage individuals to exercise caution.
- Facilitate Risk Assessment: The symbols provide a standardized framework for evaluating and understanding risks, allowing individuals to make informed decisions.
- Reduce Accidents and Injuries: By conveying information about potential dangers, these symbols help prevent accidents and injuries by encouraging safe practices.
- Enhance Communication: Hazard symbols transcend language barriers, providing a universal system for conveying safety information across cultures and languages.
- Promote Compliance: The presence of hazard symbols reinforces the importance of adhering to safety regulations and procedures.
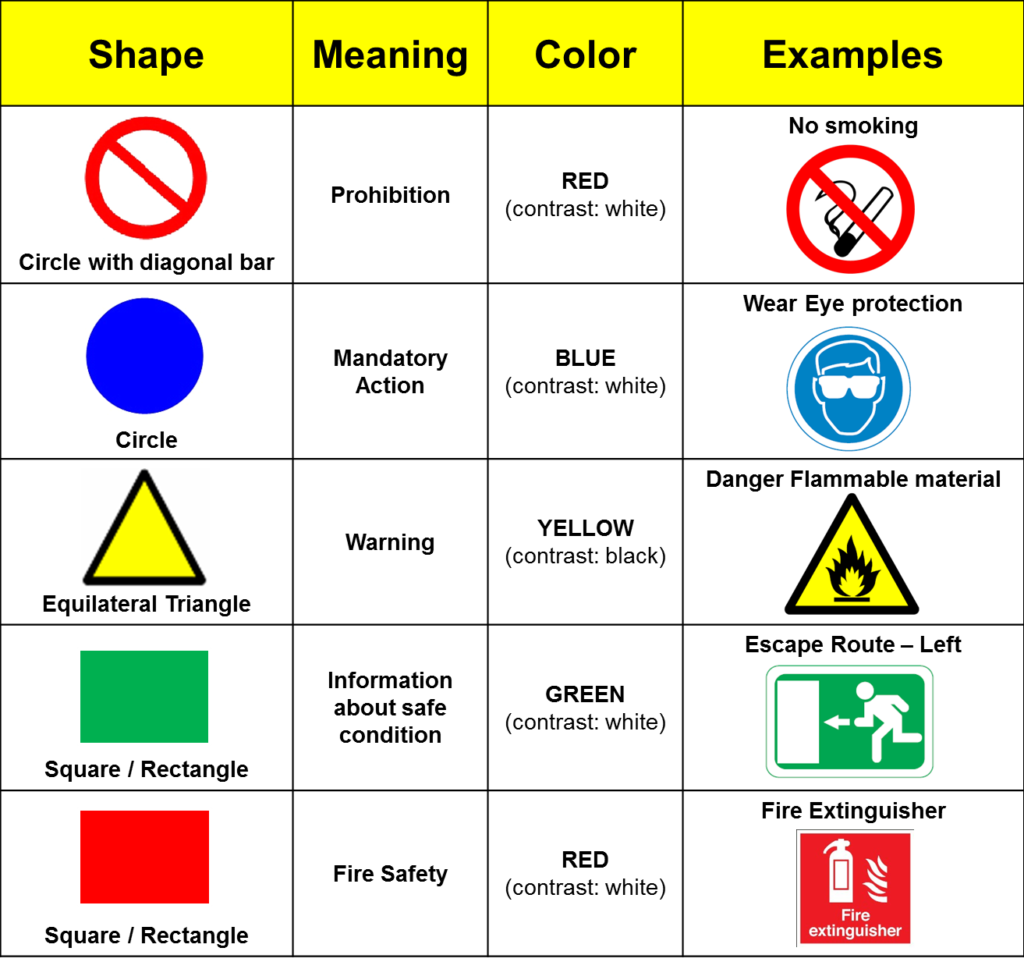
A Comprehensive Overview of Hazard Symbol Categories
Hazard symbols are broadly categorized based on the type of risk they represent. Understanding these categories is crucial for interpreting their meaning and taking appropriate precautions.
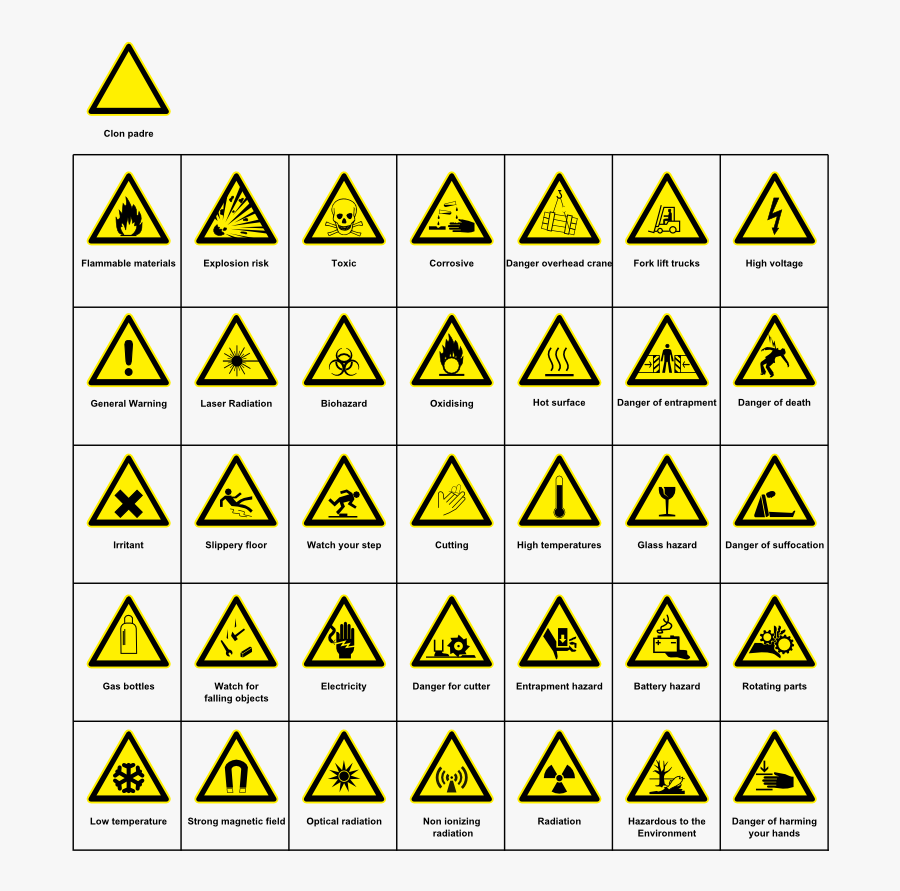
1. Chemical Hazards:
These symbols denote potential dangers associated with chemicals, including:
- Explosive Substances: This symbol, often depicted as a bomb with a burning fuse, indicates substances that can detonate or explode under certain conditions. Examples include dynamite, gunpowder, and fireworks.
- Flammable Substances: This symbol, characterized by a flame, represents substances that easily ignite and burn. Examples include gasoline, alcohol, and acetone.
- Oxidizing Substances: This symbol, often depicting a flame over a circle, signifies substances that accelerate the combustion of other materials. Examples include hydrogen peroxide and potassium permanganate.
- Corrosive Substances: This symbol, featuring a hand being eaten away, represents substances that can damage living tissues or metals. Examples include acids, alkalis, and bleach.
- Toxic Substances: This symbol, typically depicting a skull and crossbones, denotes substances that can cause harm or death through ingestion, inhalation, or skin contact. Examples include cyanide, arsenic, and mercury.
- Harmful Substances: This symbol, often depicting an exclamation mark within a circle, indicates substances that can cause harm but are not as dangerous as toxic substances. Examples include ammonia, chlorine, and formaldehyde.
2. Physical Hazards:
These symbols warn about potential dangers related to physical forces or conditions, including:
- Compressed Gases: This symbol, often depicting a cylinder with a gas escaping, signifies substances that are stored under high pressure. Examples include oxygen, nitrogen, and helium.
- Flammable Liquids: This symbol, characterized by a flame over a circle, represents liquids that easily ignite and burn. Examples include gasoline, kerosene, and acetone.
- Flammable Solids: This symbol, depicting a flame over a circle, signifies solid materials that can easily ignite and burn. Examples include wood, paper, and textiles.
- Flammable Aerosols: This symbol, depicting a flame over a circle, represents aerosols that can easily ignite and burn. Examples include hairspray, spray paint, and lighter fluid.
- Oxidizing Gases: This symbol, often depicting a flame over a circle, signifies gases that can accelerate the combustion of other materials. Examples include oxygen and chlorine.
- Corrosive Gases: This symbol, featuring a hand being eaten away, represents gases that can damage living tissues or metals. Examples include chlorine gas and sulfur dioxide.
- Toxic Gases: This symbol, typically depicting a skull and crossbones, denotes gases that can cause harm or death through inhalation. Examples include carbon monoxide, chlorine gas, and hydrogen sulfide.
- Harmful Gases: This symbol, often depicting an exclamation mark within a circle, indicates gases that can cause harm but are not as dangerous as toxic gases. Examples include ammonia gas and sulfur dioxide.
- Radioactive Materials: This symbol, depicting a trefoil (three-leaf clover), signifies materials that emit ionizing radiation. Examples include uranium, plutonium, and radium.
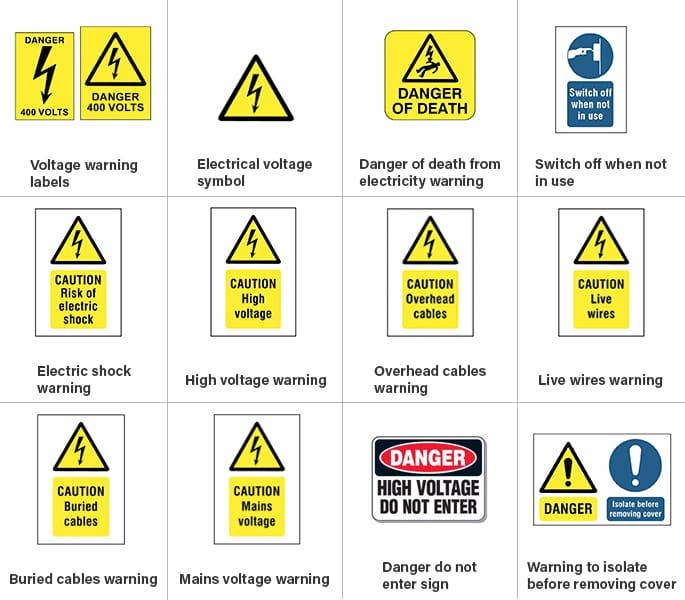
- Electrical Hazards: This symbol, depicting a lightning bolt, warns about the potential for electric shock. Examples include high-voltage lines, electrical appliances, and wiring.
- Mechanical Hazards: This symbol, often depicting a hand caught in machinery, signifies potential dangers associated with moving parts or machinery. Examples include rotating blades, gears, and belts.
- Biological Hazards: This symbol, depicting a biohazard symbol (a circle with three biohazard symbols), signifies the presence of biological agents that can cause disease. Examples include bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
3. Environmental Hazards:
These symbols warn about potential dangers to the environment, including:
- Environmental Hazards: This symbol, often depicting a tree with a slash through it, signifies materials that can harm the environment. Examples include pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers.
- Water Pollution: This symbol, depicting a fish with a slash through it, warns about substances that can pollute water resources. Examples include sewage, industrial waste, and agricultural runoff.
- Air Pollution: This symbol, depicting a tree with a slash through it, warns about substances that can pollute the air. Examples include exhaust fumes, industrial emissions, and smoke from fires.
4. Other Hazards:
These symbols represent various other potential dangers, including:
- Caution: This symbol, often depicting a yellow triangle with an exclamation point, signifies general caution and potential hazards.
- Warning: This symbol, often depicting a black triangle with an exclamation point, signifies a more serious potential hazard.
- Danger: This symbol, often depicted a red octagon with an exclamation point, signifies an immediate and serious potential hazard.
- Prohibition: This symbol, often depicting a circle with a diagonal line through it, signifies that a particular action is prohibited.
- Mandatory Action: This symbol, often depicting a circle with a white arrow pointing in a specific direction, signifies that a particular action is required.
FAQs by Hazard Symbols and Examples
Q1: What does the skull and crossbones symbol mean?
A1: The skull and crossbones symbol indicates a toxic substance that can cause harm or death through ingestion, inhalation, or skin contact. Examples include cyanide, arsenic, and mercury.
Q2: What does the flame over a circle symbol mean?
A2: The flame over a circle symbol signifies a flammable substance that easily ignites and burns. Examples include gasoline, alcohol, and acetone.
Q3: What does the lightning bolt symbol mean?
A3: The lightning bolt symbol warns about the potential for electric shock. Examples include high-voltage lines, electrical appliances, and wiring.
Q4: What does the biohazard symbol mean?
A4: The biohazard symbol signifies the presence of biological agents that can cause disease. Examples include bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Q5: What does the tree with a slash through it symbol mean?
A5: The tree with a slash through it symbol signifies materials that can harm the environment. Examples include pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers.
Tips by Hazard Symbols and Examples
- Always read and understand the hazard symbols before handling any substance or equipment.
- Follow the safety instructions provided with the substance or equipment.
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling hazardous materials.
- Store hazardous materials in a safe and secure location.
- Dispose of hazardous materials properly.
- Report any spills or leaks immediately.
- Be aware of your surroundings and potential hazards.
Conclusion by Hazard Symbols and Examples
Hazard symbols are essential components of safety communication, providing a universal language for conveying potential risks. By understanding the meaning of these symbols and adhering to safety guidelines, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of accidents, injuries, and environmental damage. Their role in promoting safety awareness, facilitating risk assessment, and enhancing communication is invaluable in creating a safer and healthier environment for all.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Silent Language of Safety: Deciphering Hazard Symbols. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!