The Science and Practice of Skin Lightening: Understanding the Role of Bleaching Agents
Related Articles: The Science and Practice of Skin Lightening: Understanding the Role of Bleaching Agents
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Science and Practice of Skin Lightening: Understanding the Role of Bleaching Agents. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Science and Practice of Skin Lightening: Understanding the Role of Bleaching Agents

The pursuit of even-toned skin is a universal desire. Hyperpigmentation, the presence of darker patches on the skin, can arise from various factors, including sun exposure, acne, hormonal fluctuations, and certain medications. While numerous treatments exist, skin bleaching agents remain a popular option for addressing these concerns. This article delves into the science behind skin bleaching, exploring its mechanisms, potential benefits, and associated risks, while emphasizing the importance of informed decision-making and responsible usage.
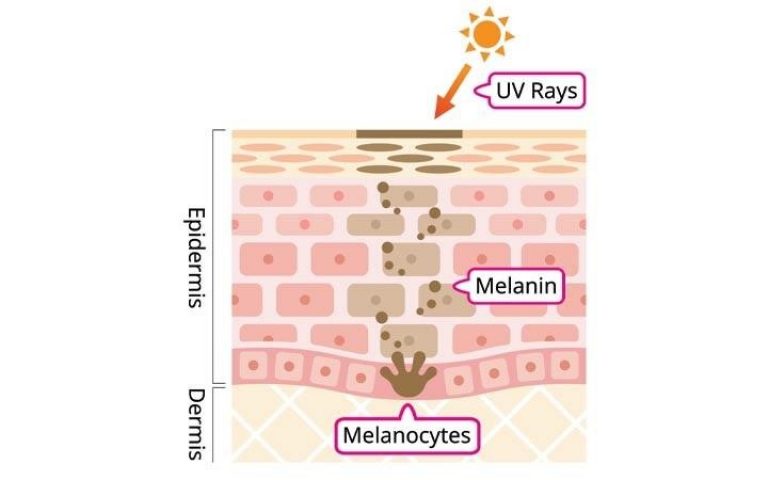
Understanding the Science of Skin Lightening
Skin pigmentation is primarily determined by the presence of melanin, a pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes. Melanin exists in two forms: eumelanin, responsible for brown to black pigmentation, and pheomelanin, contributing to reddish-yellow tones.
Skin bleaching agents work by interfering with the production or distribution of melanin within the skin. They achieve this through various mechanisms:
- Inhibition of Tyrosinase Activity: Tyrosinase is an enzyme crucial for the initial steps of melanin synthesis. Many bleaching agents, such as hydroquinone and kojic acid, act as tyrosinase inhibitors, slowing down the production of melanin.
- Disruption of Melanosome Transfer: Melanosomes are organelles that transport melanin from melanocytes to surrounding skin cells. Some agents, like azelaic acid, interfere with this transfer process, limiting the amount of melanin reaching the skin surface.
- Exfoliation and Cell Turnover: Certain bleaching agents, like retinoids, promote skin exfoliation, removing layers of pigmented skin cells and revealing underlying, lighter skin.
Common Bleaching Agents: A Closer Look
While a plethora of skin lightening products exist, certain ingredients are frequently used:
- Hydroquinone: A potent tyrosinase inhibitor, hydroquinone has been a mainstay in skin bleaching for decades. Its effectiveness is undeniable, but concerns about potential side effects, including ochronosis (a rare skin discoloration), have led to restrictions in some countries.
- Kojic Acid: Derived from certain fungi, kojic acid is another tyrosinase inhibitor. It is considered a gentler alternative to hydroquinone, with fewer reported side effects. However, its effectiveness may be less pronounced.
- Azelaic Acid: This naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid possesses both tyrosinase inhibition and anti-inflammatory properties. It is often used to treat acne and melasma, a common form of hyperpigmentation.
- Retinoids: These vitamin A derivatives are primarily known for their anti-aging effects, but they also promote cell turnover, reducing the appearance of dark spots. Retinoids are available in various strengths, with prescription-strength formulations offering greater potency.
- Niacinamide (Vitamin B3): While not a direct bleaching agent, niacinamide has shown promise in reducing hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanin transfer and improving skin barrier function.
Benefits and Considerations: Weighing the Options
Skin bleaching agents can offer several benefits:
- Reduced Hyperpigmentation: They can effectively lighten dark spots, improving skin tone and reducing the appearance of blemishes.
- Improved Skin Texture: Some agents, like retinoids, can improve skin texture by promoting cell turnover and reducing fine lines and wrinkles.
- Increased Confidence: Achieving a more even skin tone can boost self-esteem and confidence.
However, it is crucial to consider the potential drawbacks:
- Skin Irritation: Many bleaching agents can cause skin irritation, redness, dryness, and sensitivity.
- Increased Sun Sensitivity: Skin bleaching can make the skin more susceptible to sun damage.
- Potential for Long-Term Side Effects: While rare, long-term use of certain agents, like hydroquinone, can lead to ochronosis or other skin complications.
- Uneven Skin Tone: Incorrect application or overuse can result in uneven skin lightening, creating a patchy appearance.
Responsible Usage: A Guide to Safe and Effective Application
To minimize risks and maximize benefits, adhere to these guidelines:
- Consult a Dermatologist: Before using any bleaching agents, consult a qualified dermatologist to discuss your specific concerns, potential risks, and appropriate treatment options.
- Patch Test: Always perform a patch test on a small area of skin before applying any new product to your entire face. This helps identify potential allergies or sensitivities.
- Follow Instructions Carefully: Adhere to the product’s instructions regarding application frequency, dosage, and duration of use.
- Use Sunscreen: Always use sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, even on cloudy days, to protect your skin from sun damage.
- Avoid Over-Exfoliation: Excessive exfoliation can irritate the skin and make it more vulnerable to bleaching agents.
- Be Patient: Skin lightening takes time. Results may not be immediately noticeable, and consistency is key.
- Discontinue Use if Side Effects Occur: If you experience any adverse reactions, stop using the product and consult your dermatologist.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the safest way to lighten dark spots?
A: The safest approach is to consult a dermatologist for personalized advice. They can assess your skin type, the nature of your hyperpigmentation, and recommend the most suitable treatment, whether it involves over-the-counter products, prescription medications, or other procedures like chemical peels or lasers.
Q: Can I use skin bleaching products during pregnancy or breastfeeding?
A: It is generally not recommended to use skin bleaching agents during pregnancy or breastfeeding due to the potential risks to the developing fetus or infant. Consult your doctor or a qualified healthcare provider for guidance on safe skincare practices during these periods.
Q: How long does it take to see results from skin bleaching?
A: The time it takes to see results varies depending on the severity of hyperpigmentation, the type of product used, and individual skin response. It may take several weeks or even months to achieve noticeable improvement.
Q: Can I use skin bleaching products on all areas of my body?
A: Some bleaching agents are designed specifically for facial use, while others can be used on other body parts. Always follow the product’s instructions and consult your dermatologist for guidance on appropriate use.
Q: Is it possible to permanently lighten dark spots?
A: While skin bleaching can significantly reduce the appearance of dark spots, it is not typically a permanent solution. Melanin production is an ongoing process, and continued sun exposure can contribute to the recurrence of hyperpigmentation.
Tips for Effective Skin Lightening
- Protect Your Skin from the Sun: Sun exposure is a major contributor to hyperpigmentation. Always wear sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, even on cloudy days, and avoid prolonged sun exposure, especially during peak hours.
- Maintain a Consistent Skincare Routine: A regular skincare routine that includes gentle cleansing, moisturizing, and exfoliation can help maintain healthy skin and support the effectiveness of bleaching agents.
- Hydrate Your Skin: Proper hydration is essential for healthy skin. Drink plenty of water and use a hydrating moisturizer to keep your skin supple and prevent dryness, which can worsen hyperpigmentation.
- Consider Other Treatments: Skin bleaching is not the only solution for hyperpigmentation. Other options include chemical peels, laser treatments, microdermabrasion, and topical creams containing ingredients like retinol or vitamin C.
Conclusion
Skin bleaching agents can be effective in reducing the appearance of dark spots, but it is crucial to approach their use with caution and responsibility. Consulting a dermatologist, understanding the potential risks and benefits, and adhering to safe usage guidelines are paramount for achieving desired results while minimizing the risk of adverse effects. Remember that a holistic approach to skin health, including sun protection, consistent skincare, and a healthy lifestyle, is essential for maintaining a radiant and even skin tone.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Science and Practice of Skin Lightening: Understanding the Role of Bleaching Agents. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!