The Role of Hydrochloric Acid in Digestion: A Deeper Dive into Our Stomach’s Secret Weapon
Related Articles: The Role of Hydrochloric Acid in Digestion: A Deeper Dive into Our Stomach’s Secret Weapon
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Role of Hydrochloric Acid in Digestion: A Deeper Dive into Our Stomach’s Secret Weapon. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Role of Hydrochloric Acid in Digestion: A Deeper Dive into Our Stomach’s Secret Weapon
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Role of Hydrochloric Acid in Digestion: A Deeper Dive into Our Stomach’s Secret Weapon
- 3.1 The Stomach’s Acidic Environment: A Necessary Evil
- 3.2 The Importance of Maintaining Optimal Stomach Acid Levels
- 3.3 Factors Affecting Stomach Acid Production
- 3.4 Addressing Stomach Acid Imbalances
- 3.5 FAQs about Hydrochloric Acid in Digestion
- 3.6 Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Role of Hydrochloric Acid in Digestion: A Deeper Dive into Our Stomach’s Secret Weapon
Hydrochloric acid (HCl), a potent chemical compound, is often associated with corrosive materials and industrial processes. However, this same acid plays a vital role in our digestive system, serving as a key player in breaking down food and ensuring proper nutrient absorption.
While it is not directly found in food itself, understanding its production and function within the stomach is crucial to appreciating the intricate workings of our digestive system.
The Stomach’s Acidic Environment: A Necessary Evil
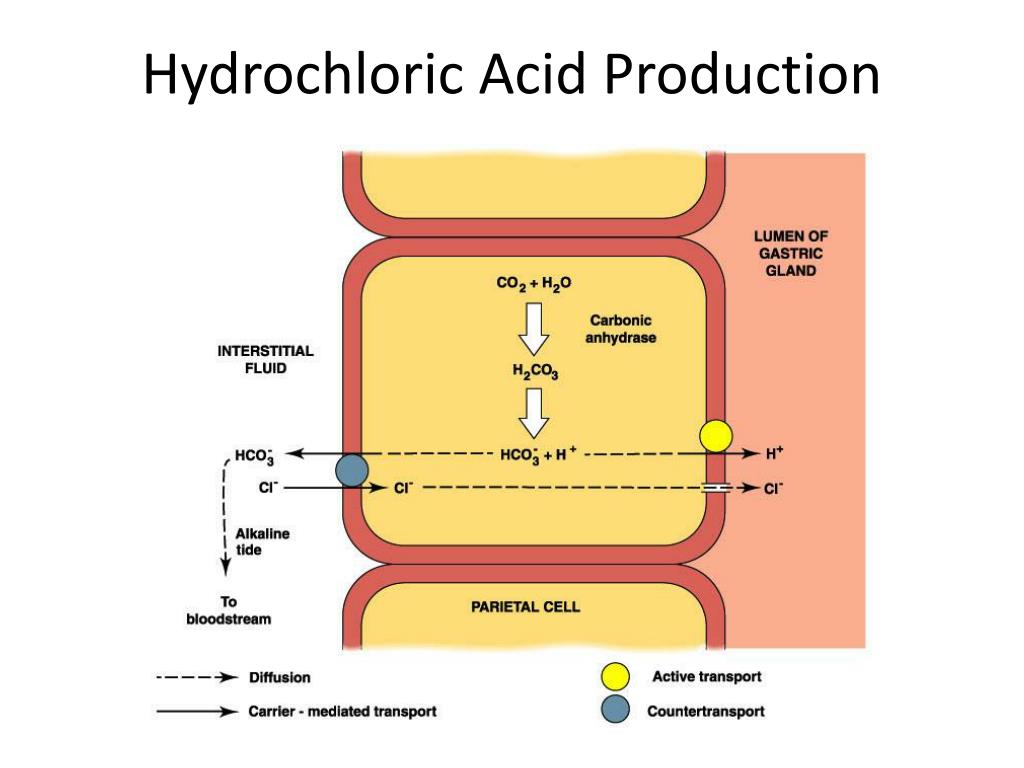
The stomach is a muscular organ responsible for initial food breakdown. Its lining, protected by a thick layer of mucus, harbors specialized cells that produce hydrochloric acid. This acid, along with digestive enzymes, creates a highly acidic environment with a pH ranging from 1.5 to 3.5, a level comparable to that of battery acid.
This acidic environment serves several crucial functions:
- Denaturation of Proteins: HCl disrupts the complex structure of proteins, unfolding them into simpler chains, making them more accessible to digestive enzymes. This process, known as denaturation, is essential for the breakdown of proteins into their constituent amino acids, the building blocks of our bodies.
- Activation of Pepsinogen: Pepsinogen, an inactive enzyme produced by the stomach lining, is converted into its active form, pepsin, in the presence of HCl. Pepsin, a protease, is responsible for breaking down proteins into smaller peptides.
- Killing Bacteria and Pathogens: The acidic environment of the stomach acts as a natural barrier against harmful bacteria and pathogens ingested with food. This antimicrobial activity prevents infections and safeguards our health.
- Mineral Absorption: HCl aids in the absorption of essential minerals like iron and calcium, facilitating their transport into the bloodstream.
The Importance of Maintaining Optimal Stomach Acid Levels
While crucial for digestion, maintaining the right balance of stomach acid is critical for overall health.
- Hypochlorhydria (Low Stomach Acid): Insufficient production of stomach acid can lead to indigestion, bloating, and malabsorption of nutrients, particularly proteins, iron, and B12. This condition can also increase the risk of bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine, leading to further digestive issues.
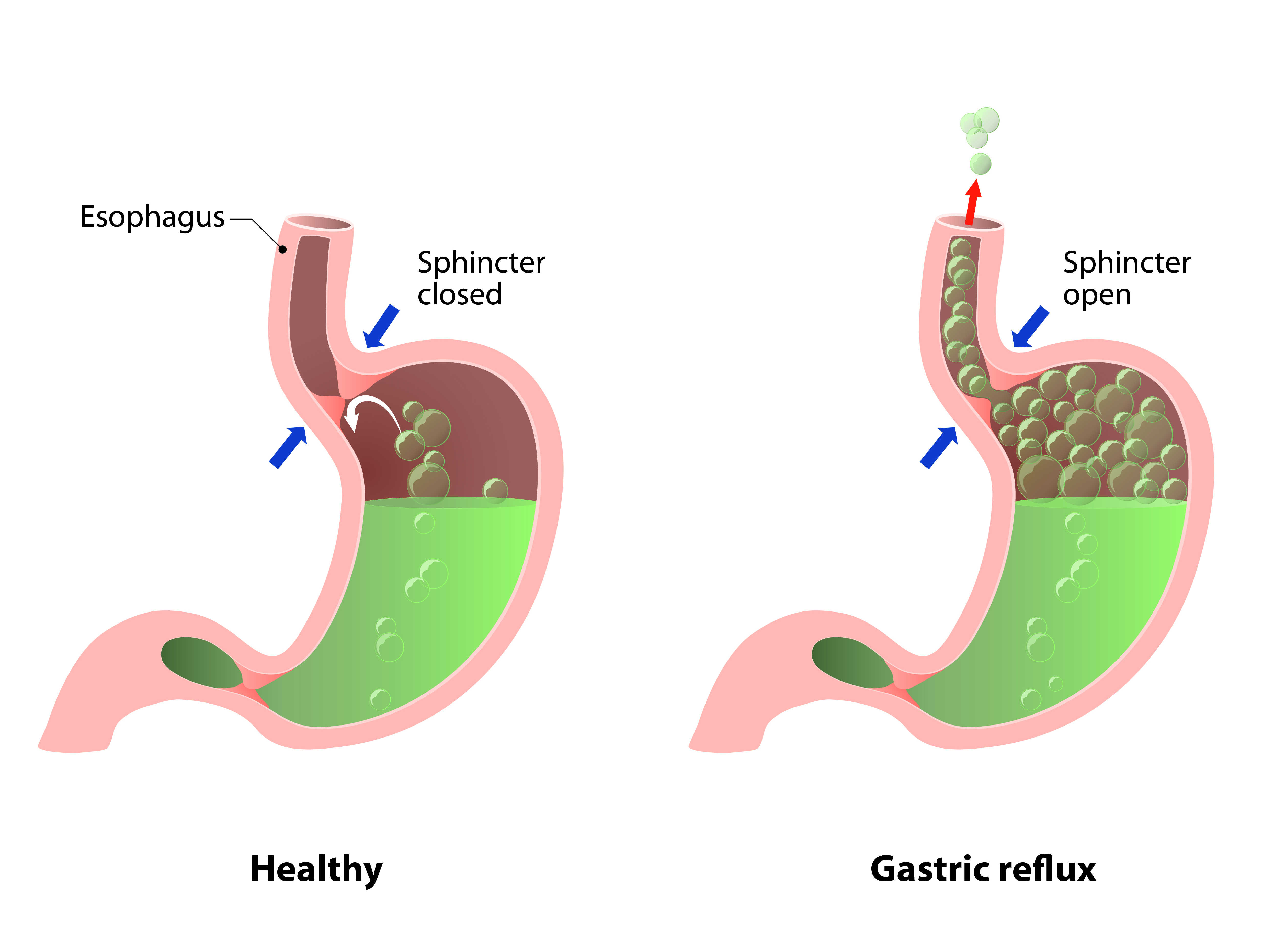
- Hyperchlorhydria (Excess Stomach Acid): Excessive stomach acid production can result in heartburn, acid reflux, and ulcers. While rare, this condition can be caused by factors like stress, certain medications, or certain medical conditions.
Factors Affecting Stomach Acid Production
Several factors can influence the production of stomach acid, including:
- Age: Stomach acid production naturally declines with age, potentially contributing to digestive issues in older adults.
- Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt the delicate balance of stomach acid production, leading to both hypo- and hyperchlorhydria.
- Diet: A diet low in protein and fiber can reduce stomach acid production, while a diet rich in spicy foods, alcohol, and caffeine can stimulate its production.
- Medications: Certain medications, including antacids, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), and antibiotics, can interfere with stomach acid production.
Addressing Stomach Acid Imbalances
If you suspect an imbalance in your stomach acid production, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Addressing Hypochlorhydria:
- Dietary Adjustments: Incorporating protein-rich foods, fermented foods, and apple cider vinegar into your diet can help increase stomach acid production.
- Supplementation: Hydrochloric acid supplements, available in various forms, can be used to replenish low stomach acid levels.
- Lifestyle Changes: Managing stress levels through techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can positively impact stomach acid production.
Addressing Hyperchlorhydria:
- Dietary Modifications: Avoiding trigger foods like spicy foods, coffee, alcohol, and citrus fruits can help manage excess stomach acid.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking, and eating smaller, more frequent meals can reduce the risk of heartburn and acid reflux.
- Medications: Antacids and PPIs can be used to neutralize excess stomach acid, but long-term use should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
FAQs about Hydrochloric Acid in Digestion
Q: Can I increase stomach acid production naturally?
A: Yes, incorporating protein-rich foods, fermented foods, and apple cider vinegar into your diet can help. Engaging in stress management techniques can also positively impact stomach acid production.
Q: What are the symptoms of low stomach acid?
A: Symptoms include indigestion, bloating, gas, heartburn, food intolerances, and nutrient deficiencies.
Q: What are the symptoms of high stomach acid?
A: Symptoms include heartburn, acid reflux, nausea, vomiting, and ulcers.
Q: Can I take hydrochloric acid supplements?
A: Hydrochloric acid supplements are available over the counter, but it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional before taking them, as they may not be suitable for everyone.
Q: Can I use apple cider vinegar to increase stomach acid?
A: Apple cider vinegar is a popular home remedy for low stomach acid, but its effectiveness is not scientifically proven. It’s best to consult a healthcare professional before using it for this purpose.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to aid digestion.
- Manage stress: Stress can disrupt digestion; engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption: These habits can damage the stomach lining and interfere with digestion.
- Be mindful of your eating habits: Eat slowly, chew your food thoroughly, and avoid overeating.
- Consult a healthcare professional if you experience persistent digestive issues: Early intervention can prevent complications and ensure optimal digestive health.
Conclusion
Hydrochloric acid, while often associated with corrosive substances, plays a vital role in our digestive system. Its presence in the stomach is essential for protein breakdown, nutrient absorption, and protection against harmful bacteria. Maintaining a healthy balance of stomach acid is crucial for optimal digestion and overall well-being. By understanding the factors influencing stomach acid production and making informed dietary and lifestyle choices, we can support a healthy digestive system and enjoy the benefits of efficient nutrient absorption and a robust immune system.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Role of Hydrochloric Acid in Digestion: A Deeper Dive into Our Stomach’s Secret Weapon. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!