The Foundation of Financial Security: Understanding Household Assets
Related Articles: The Foundation of Financial Security: Understanding Household Assets
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Foundation of Financial Security: Understanding Household Assets. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Foundation of Financial Security: Understanding Household Assets

Household assets represent the tangible and intangible possessions that individuals and families own. These assets serve as a cornerstone of financial security, providing a safety net during times of economic hardship and contributing to long-term wealth accumulation. Understanding the diverse nature and value of household assets is crucial for informed financial planning, investment decisions, and overall well-being.
Defining the Scope of Household Assets:
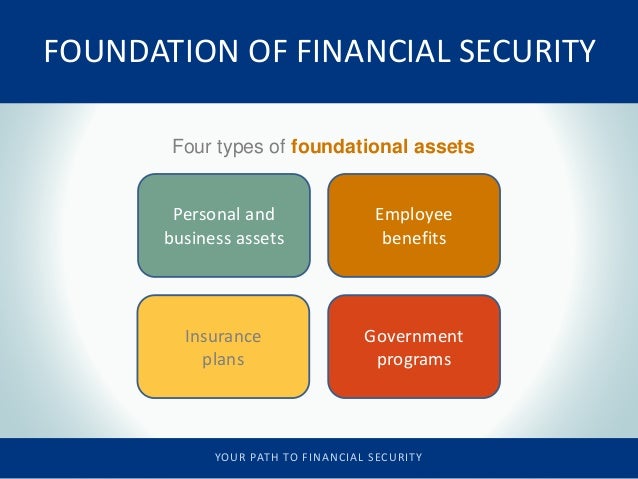
Household assets encompass a broad spectrum of possessions, ranging from readily marketable items to less liquid investments. They can be categorized as follows:
1. Real Estate:
- Primary Residence: The primary dwelling where an individual or family resides is often the most significant asset in their portfolio. Its value fluctuates with market conditions and can be a source of equity for future investments or financial needs.
- Investment Properties: Additional properties owned for rental income or potential appreciation are considered investment assets. Their value and income streams contribute to the overall financial strength of the household.
2. Financial Assets:
- Cash and Equivalents: Liquid assets like savings accounts, checking accounts, and money market funds provide immediate access to funds for daily expenses and emergencies.
- Investments: Stocks, bonds, mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and other securities represent investments in companies or financial instruments. They offer the potential for growth and income generation, but also carry inherent risks.
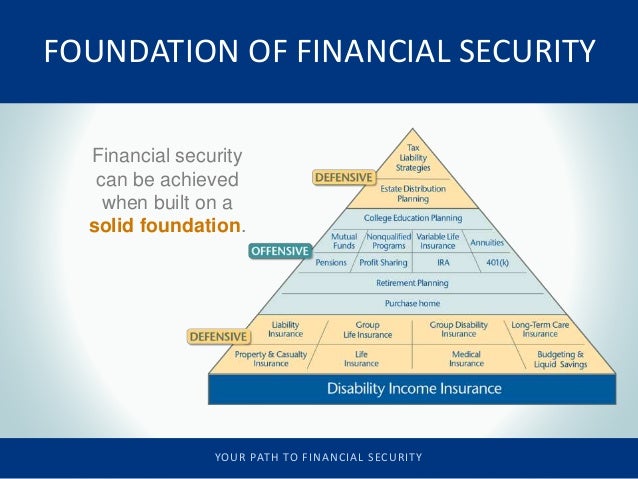
- Retirement Accounts: 401(k)s, IRAs, and other retirement savings plans are designed for long-term financial security and are generally tax-advantaged. Their value fluctuates based on market performance and investment choices.
- Annuities: These contracts provide a stream of income for a specific period or for life, offering a guaranteed income stream for retirement or other financial planning purposes.
3. Personal Property:
- Vehicles: Cars, trucks, motorcycles, and other vehicles are often considered major assets, though their value depreciates over time.
- Jewelry and Precious Metals: Gold, silver, and other precious metals can serve as a store of value and hedge against inflation, but their liquidity can vary depending on market conditions.
- Collectibles: Art, antiques, stamps, coins, and other collectible items can appreciate in value over time, but their marketability and valuation can be subjective.
- Household Furnishings and Appliances: While these items are essential for daily living, they generally have lower market value and depreciate quickly.
4. Intangible Assets:
- Human Capital: An individual’s education, skills, and experience represent a valuable asset that contributes to their earning potential and career advancement.
- Intellectual Property: Patents, copyrights, trademarks, and other forms of intellectual property can generate revenue and provide competitive advantages in business or creative endeavors.
- Social Capital: Networks of relationships, connections, and reputation can be valuable assets for business opportunities, career advancement, and personal growth.
The Importance of Household Assets:
Household assets play a vital role in financial security and well-being by providing:
- Financial Stability: Assets serve as a buffer against unexpected financial shocks, such as job loss, medical emergencies, or economic downturns.
- Investment Opportunities: Assets can be leveraged for investment purposes, allowing for wealth accumulation and potential income generation.
- Retirement Security: Assets, particularly retirement savings plans, are crucial for funding a comfortable retirement and ensuring financial independence in later years.
- Debt Management: Assets can be used as collateral for loans, potentially securing lower interest rates and facilitating debt consolidation.
- Intergenerational Wealth Transfer: Assets can be passed down to future generations, providing a legacy of financial security and opportunity.
Factors Influencing Asset Value:
The value of household assets is dynamic and influenced by various factors, including:
- Market Conditions: Economic fluctuations, interest rates, inflation, and real estate market trends can significantly impact asset values.
- Investment Choices: The performance of investments, such as stocks or bonds, is influenced by market volatility and investment strategies.
- Maintenance and Upkeep: Regular maintenance and upkeep of real estate and personal property can preserve value and minimize depreciation.
- Inflation: The purchasing power of assets can be eroded by inflation, making it crucial to consider asset allocation strategies to mitigate this risk.
- Taxation: Capital gains taxes on asset sales and other tax implications can impact the overall value of assets.
FAQs on Household Assets:
Q: What is the difference between assets and liabilities?
A: Assets are what you own, while liabilities are what you owe. Assets represent resources that can be used to generate income or provide value, while liabilities represent financial obligations that need to be repaid.
Q: How do I determine the value of my assets?
A: The value of assets can be determined through various methods:
- Market Value: This is the price at which an asset could be sold in a competitive market.
- Appraisal: A professional appraisal can provide an objective assessment of an asset’s value.
- Tax Assessments: Local government assessments of real estate values can serve as a benchmark.
- Financial Statements: Banks and investment firms provide statements that reflect the current value of financial assets.
Q: How do I manage my household assets effectively?
A: Effective asset management involves:
- Diversification: Spreading investments across different asset classes to reduce risk.
- Rebalancing: Adjusting the asset allocation periodically to maintain a desired risk profile.
- Monitoring and Review: Regularly reviewing asset performance and making adjustments as needed.
- Professional Advice: Consulting with a financial advisor can provide personalized guidance and support.
Tips for Building and Managing Household Assets:
- Start Early: Begin saving and investing early to benefit from compound interest and long-term growth.
- Budget and Track Expenses: Develop a realistic budget and track expenses to identify areas for savings and investment.
- Pay Down Debt: Prioritize paying down high-interest debt to free up cash flow for savings and investments.
- Automate Savings: Set up automatic transfers to savings accounts and retirement plans to ensure consistent contributions.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult with a financial advisor to develop a personalized plan for building and managing assets.
Conclusion:
Household assets represent the foundation of financial security and well-being. Understanding the diverse nature, value, and management of these assets is crucial for informed financial planning, investment decisions, and overall financial stability. By prioritizing asset building, managing them effectively, and seeking professional guidance, individuals and families can create a strong financial foundation for a secure future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Foundation of Financial Security: Understanding Household Assets. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!