The Essential Element: Exploring the Role of Boron in Borax
Related Articles: The Essential Element: Exploring the Role of Boron in Borax
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Essential Element: Exploring the Role of Boron in Borax. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Essential Element: Exploring the Role of Boron in Borax

Borax, a naturally occurring mineral compound, has a long history of use in various applications, from household cleaning to industrial processes. Its chemical composition, however, is often a source of confusion. Many wonder: Does borax contain boron? The answer, unequivocally, is yes. Borax, in fact, is a primary source of boron.
Understanding the Chemistry of Borax
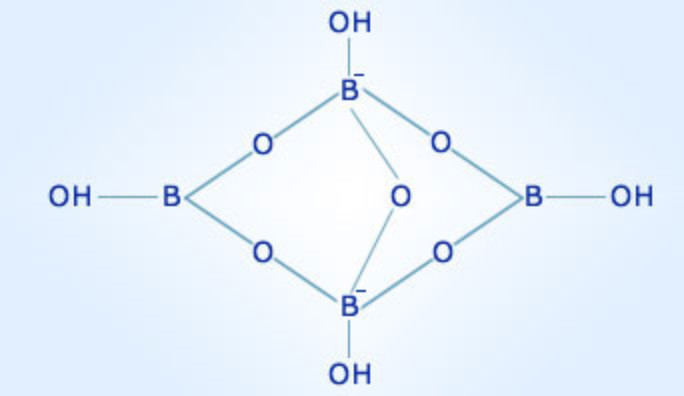
Borax, chemically known as sodium borate decahydrate (Na₂B₄O₇·10H₂O), is a white, crystalline compound that contains boron as a key element. The boron atoms in borax are present in the form of borate anions (B₄O₇²⁻), which are complex structures composed of boron and oxygen atoms. These borate anions are responsible for many of borax’s unique properties.
The Significance of Boron in Borax
Boron, a metalloid element, plays a crucial role in the properties and applications of borax. It contributes to:
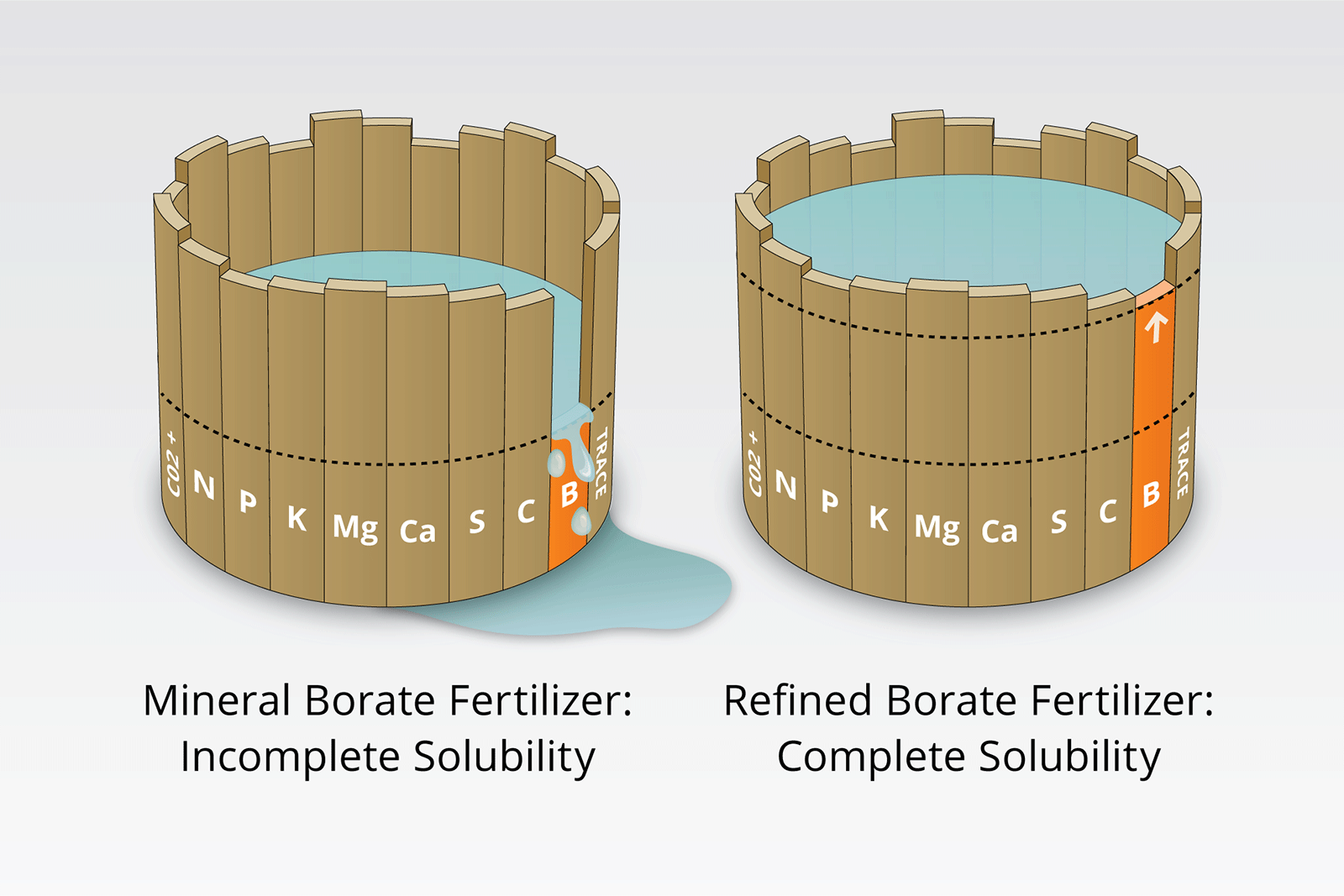
- Water solubility: Borax dissolves readily in water, a characteristic that makes it suitable for various cleaning and industrial applications.
- Antiseptic properties: Borax exhibits antimicrobial properties, making it effective in inhibiting the growth of bacteria and fungi. This property makes it a popular ingredient in certain cleaning products.
- Buffering capacity: Borax can act as a buffer, maintaining a relatively stable pH level in solutions. This property is useful in industries like cosmetics and pharmaceuticals.
- Flame retardancy: Boron compounds, including borax, are known for their flame retardant properties. This makes borax a valuable component in fire-resistant materials.
Beyond Cleaning: Applications of Borax and Boron
While borax is commonly associated with household cleaning, its applications extend far beyond this domain. Boron, derived from borax, finds its way into numerous industries, including:
- Agriculture: Boron is an essential micronutrient for plant growth. It plays a vital role in cell wall formation, pollen development, and sugar transport. Borax is used as a boron fertilizer to improve crop yields and quality.
- Glass and ceramics: Boron compounds are key ingredients in the manufacture of various types of glass, including borosilicate glass (Pyrex). They enhance the durability and heat resistance of these materials. Borax is also used in glazes and enamels for ceramics, contributing to their color and shine.
- Industrial applications: Borax is used in numerous industrial processes, including the production of detergents, soaps, and other cleaning agents. It is also used in the manufacture of textile dyes, leather tanning, and metalworking.
- Medicine and pharmaceuticals: Boron compounds are used in some pharmaceuticals, particularly in the treatment of arthritis and other inflammatory conditions. They are also used as antiseptics and disinfectants.
FAQs: Exploring the Importance of Boron in Borax
Q1: Is borax safe to use in the home?
A: Borax is generally considered safe when used in appropriate amounts and with proper precautions. However, it is important to keep borax out of reach of children and pets, as ingestion can be harmful. It is also advisable to wear gloves and eye protection when handling borax.
Q2: What are the potential health risks associated with borax?
A: Prolonged or excessive exposure to borax can lead to health problems. Ingestion of large quantities can cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Inhalation of borax dust can irritate the respiratory system. Some studies have suggested potential links between borax exposure and reproductive problems, but further research is needed to confirm these findings.
Q3: Is borax a natural mineral?
A: Yes, borax is a naturally occurring mineral compound. It is extracted from deposits found in various parts of the world, including the United States, Turkey, and Chile.
Q4: How is borax extracted and processed?
A: Borax is typically extracted from deposits using a process called open-pit mining. The ore is crushed and then dissolved in water. The solution is then treated to remove impurities and concentrate the borax. The concentrated borax solution is then crystallized and dried to produce the final product.
Q5: What are some alternative cleaning products that can be used instead of borax?
A: There are several alternative cleaning products available that can be used instead of borax. These include baking soda, vinegar, and commercially available cleaning solutions.
Tips for Using Borax Safely and Effectively
- Use borax in moderation: Avoid using excessive amounts of borax, as this can lead to health risks.
- Keep borax out of reach of children and pets: Store borax in a secure location where it cannot be accessed by children or pets.
- Wear gloves and eye protection when handling borax: Protect your skin and eyes from contact with borax dust.
- Use borax in well-ventilated areas: Ensure adequate ventilation when using borax, especially in enclosed spaces.
- Avoid mixing borax with other chemicals: Mixing borax with other chemicals, such as bleach, can create harmful fumes.
Conclusion
Borax, a naturally occurring mineral compound, is a significant source of boron, an element essential for various applications. From its role in plant growth and industrial processes to its use in cleaning products and pharmaceuticals, boron’s impact is multifaceted. While borax can be a valuable resource, it is crucial to use it responsibly and with awareness of its potential health risks. By understanding the chemistry and applications of borax, we can leverage its benefits while ensuring its safe and sustainable use.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Essential Element: Exploring the Role of Boron in Borax. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!