Reimagining Waste: A Comprehensive Guide to Reuse
Related Articles: Reimagining Waste: A Comprehensive Guide to Reuse
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Reimagining Waste: A Comprehensive Guide to Reuse. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Reimagining Waste: A Comprehensive Guide to Reuse
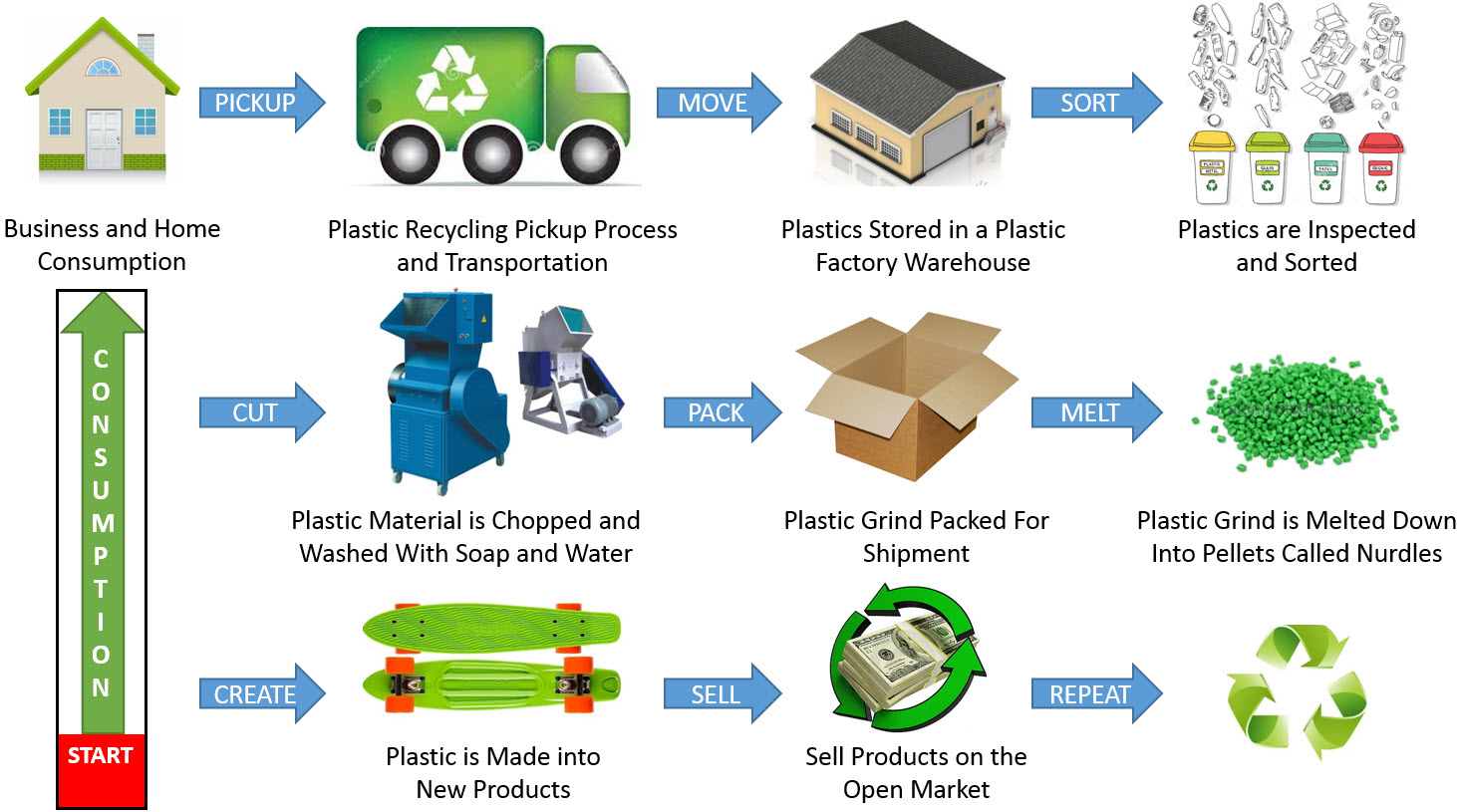
In an era of escalating environmental concerns, the concept of "reuse" has emerged as a potent tool for sustainable living. It involves repurposing discarded materials or objects, giving them a new life and reducing the demand for virgin resources. This practice not only mitigates environmental impact but also offers economic and social benefits, fostering a circular economy and promoting resource conservation.
This article explores the diverse realm of reuse, delving into various examples across different sectors and highlighting the multifaceted advantages it presents.
Examples of Reuse Across Sectors:
1. Household Reuse:
- Upcycling Furniture: Old chairs, tables, and cabinets can be transformed into unique pieces through sanding, painting, and creative embellishments.
- Repurposing Glass Jars: Glass jars, commonly used for food storage, can be reused as planters for herbs, candles, or decorative elements.
- Clothing and Textiles: Old clothing can be repurposed into quilts, bags, or even new garments through techniques like upcycling and mending.
- Paper and Cardboard: Used paper can be recycled into new paper products, while cardboard boxes can be used for storage, crafting, or even building materials.
2. Industrial Reuse:
- Construction and Demolition Waste: Debris from construction and demolition projects can be reused as aggregate in road construction or as backfill for landscaping.
- Scrap Metal: Scrap metal from manufacturing processes can be melted down and recast into new products, reducing the need for mining.
- Industrial Byproducts: Byproducts from industrial processes, such as sawdust or fly ash, can be used in construction materials or as soil amendments.
- Pallet Reuse: Wooden pallets are often discarded after use, but they can be repurposed for building furniture, fences, or even garden structures.
3. Electronic Reuse:
- Re-manufacturing: Electronic devices, such as laptops and smartphones, can be disassembled, repaired, and remanufactured into functional units.
- Data Recovery: Data stored on old hard drives can be recovered and reused for various purposes, such as archiving or research.
- Component Reuse: Components from old electronic devices, like memory chips or batteries, can be salvaged and used in new devices.
- E-waste Recycling: Electronic waste can be responsibly recycled, extracting valuable materials and minimizing environmental pollution.
4. Food and Packaging Reuse:
- Composting Food Waste: Food scraps can be composted to create nutrient-rich soil amendments for gardens and landscapes.
- Reusable Food Containers: Glass or stainless steel containers can replace single-use plastic containers for storing and transporting food.
- Reusable Shopping Bags: Cloth or canvas bags can replace plastic bags, reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
- Upcycled Food Packaging: Used food packaging, like cardboard boxes or plastic containers, can be used for crafts, storage, or even repurposed as planters.
Benefits of Reuse:
1. Environmental Benefits:
- Resource Conservation: Reuse significantly reduces the need for extracting new raw materials, conserving finite resources like minerals, timber, and water.
- Waste Reduction: By repurposing discarded materials, reuse minimizes the amount of waste sent to landfills, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and land pollution.
- Energy Savings: Manufacturing new products from virgin materials requires substantial energy input. Reuse reduces this energy demand, contributing to a more sustainable energy system.
- Reduced Pollution: Extraction and processing of raw materials often generate air, water, and soil pollution. Reuse minimizes these environmental impacts.
2. Economic Benefits:
- Cost Savings: Reusing materials can be significantly cheaper than purchasing new ones, leading to cost savings for businesses and individuals.
- Job Creation: The reuse industry creates new jobs in areas like repair, refurbishment, and remanufacturing, contributing to local economies.
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Reuse fosters innovation and entrepreneurship, encouraging the development of new products and services based on repurposed materials.
- Increased Market Value: Reused items often have a higher market value than new ones, particularly in sectors like vintage furniture or antique clothing.
3. Social Benefits:
- Community Empowerment: Reuse initiatives can empower communities by promoting self-sufficiency and resourcefulness, fostering a sense of shared responsibility for environmental stewardship.
- Social Equity: Reuse programs can provide access to affordable goods and services for low-income communities, promoting social equity and inclusion.
- Cultural Preservation: Reusing items with historical or cultural significance helps preserve cultural heritage and traditions.
- Educational Value: Reuse practices can serve as educational tools, raising awareness about environmental issues and promoting sustainable living habits.
FAQs on Reuse:
Q: What is the difference between reuse and recycling?
A: Reuse involves giving an item a new life without changing its form, while recycling involves transforming materials into new products. For example, reusing a glass jar as a planter is reuse, while melting down glass bottles to create new glass is recycling.
Q: How can I start reusing items at home?
A: Begin by assessing your current belongings and identifying items that can be repurposed. Consider upcycling furniture, repurposing old clothing, or using glass jars for storage.
Q: Are there any safety concerns associated with reusing materials?
A: It is important to be aware of potential safety hazards when reusing materials. For example, old paint may contain lead, and electronic waste may contain hazardous substances. Proper research and safety precautions are essential.
Q: How can I find information about reuse initiatives in my area?
A: Contact your local waste management agency, environmental organizations, or community centers to inquire about reuse programs and resources.
Tips for Effective Reuse:
- Think creatively: Explore different ways to repurpose items, considering their potential uses beyond their original function.
- Research materials: Learn about the materials used in products and potential hazards associated with reuse.
- Clean and sanitize: Thoroughly clean and sanitize reused items before using them, especially for food storage or personal care.
- Support local reuse businesses: Patronize businesses that specialize in reuse, repair, and refurbishment, promoting a circular economy.
- Educate and inspire: Share your knowledge about reuse with others, encouraging them to adopt sustainable practices.
Conclusion:
Reuse is a powerful tool for mitigating environmental impact, fostering economic growth, and promoting social equity. By reimagining waste as a resource, we can create a more sustainable future where resources are used efficiently, and waste is minimized. From upcycling furniture to reusing electronic components, the possibilities for reuse are endless, encouraging innovation, creativity, and a renewed appreciation for the value of materials. Embracing reuse is not just a choice but a responsibility, a commitment to a greener, more equitable, and resource-conscious future.



![]()



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Reimagining Waste: A Comprehensive Guide to Reuse. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!