Navigating the World of Hazardous Materials: A Comprehensive Guide to HHPS and WHMIS Symbols
Related Articles: Navigating the World of Hazardous Materials: A Comprehensive Guide to HHPS and WHMIS Symbols
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World of Hazardous Materials: A Comprehensive Guide to HHPS and WHMIS Symbols. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World of Hazardous Materials: A Comprehensive Guide to HHPS and WHMIS Symbols

The world of chemicals and hazardous materials is a complex and potentially dangerous landscape. To ensure the safety of workers, consumers, and the environment, comprehensive systems of classification and communication are essential. Two such systems, the Hazardous Products Information System (HHPS) and the Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS), play a crucial role in providing clear and concise information about the potential hazards associated with various substances.
The Importance of Standardized Systems
Before delving into the specifics of HHPS and WHMIS, it is crucial to understand the need for standardized systems in managing hazardous materials. Without clear and consistent communication about the risks involved, the potential for accidents, injuries, and environmental damage increases significantly. These systems provide a common language and framework for understanding and managing hazards, enabling:
- Effective Hazard Communication: Clear and consistent labeling and documentation allow workers, consumers, and emergency responders to quickly identify the potential dangers associated with a product.
- Informed Decision-Making: By providing detailed information about the hazards and appropriate handling procedures, these systems empower individuals to make informed decisions about their safety and the safety of others.
- Improved Safety Practices: The use of standardized symbols and information promotes a culture of safety awareness, encouraging individuals to adopt safe work practices and take necessary precautions.
- Enhanced Environmental Protection: By understanding the potential environmental impacts of hazardous materials, individuals can take steps to minimize their release and ensure responsible disposal.
HHPS: The Foundation of Hazard Information
The Hazardous Products Information System (HHPS) serves as the bedrock for hazard communication in Canada. It provides a comprehensive framework for classifying hazardous products based on their inherent risks and developing standardized labels, safety data sheets (SDS), and other communication materials.
Key Elements of HHPS:
-
Hazard Classes: HHPS categorizes hazardous products into 10 distinct hazard classes, each representing a specific type of risk:
- Class 1: Explosives: Substances that can detonate or rapidly decompose under certain conditions.
- Class 2: Gases: Substances that exist as gases at normal temperatures and pressures, posing risks of flammability, toxicity, or reactivity.
- Class 3: Flammable Liquids: Liquids that readily ignite and pose fire hazards.
- Class 4: Flammable Solids: Solids that ignite easily and pose fire hazards.
- Class 5: Oxidizers and Organic Peroxides: Substances that can accelerate combustion or decompose explosively.
- Class 6: Toxic and Infectious Substances: Substances that can cause harm through ingestion, inhalation, or skin contact.
- Class 7: Radioactive Materials: Substances that emit ionizing radiation, posing health risks.
- Class 8: Corrosives: Substances that can damage skin, eyes, and other materials.
- Class 9: Miscellaneous Hazardous Substances: Substances that do not fit into the other classes but pose significant hazards.
- Class 10: Environmentally Hazardous Substances: Substances that pose risks to the environment.
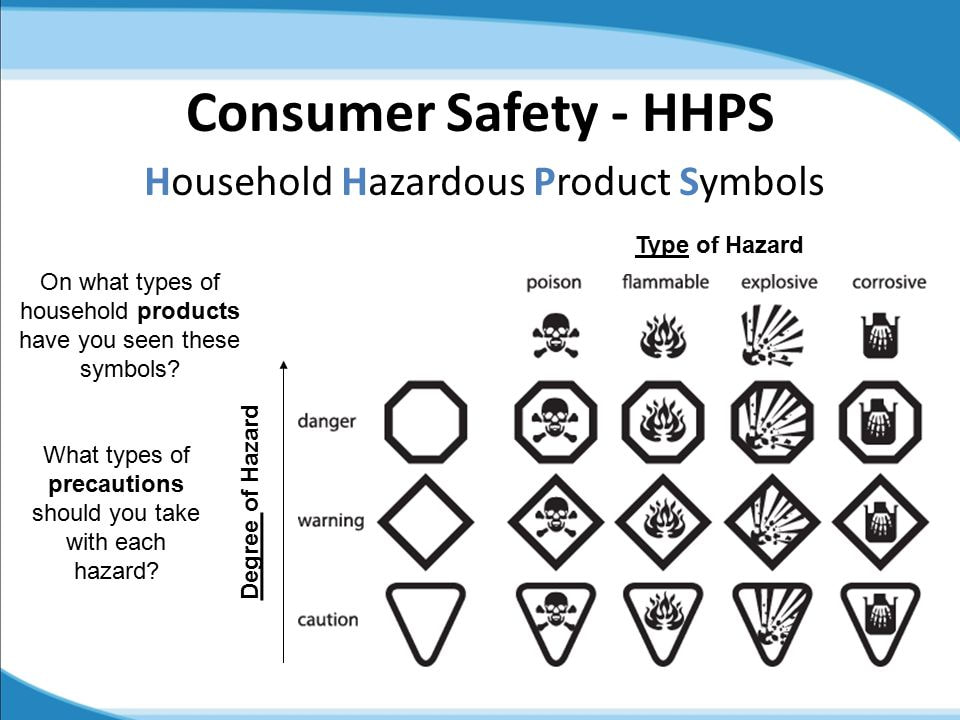
- Hazard Symbols: Each hazard class is represented by a distinct symbol, providing a visual cue to the potential risks associated with a product. These symbols are universally recognized and serve as a quick and easy way to identify hazards.
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS): SDSs are comprehensive documents that provide detailed information about a hazardous product, including its chemical composition, physical properties, health hazards, environmental risks, and handling and emergency procedures.
WHMIS: Bringing Hazard Information to the Workplace
The Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS) builds upon the foundation laid by HHPS, applying its principles to the specific context of the workplace. WHMIS ensures that workers are adequately informed about the hazards they may encounter in their work environment and are equipped with the knowledge and training necessary to work safely.
Key Elements of WHMIS:
- Workplace Labeling: WHMIS requires that all hazardous materials in the workplace be properly labeled with information about the product, its hazards, and any necessary precautions.
- SDS Availability: Employers are obligated to provide readily accessible SDSs for all hazardous products used in the workplace.
- Worker Training: WHMIS mandates that workers receive comprehensive training on the hazards associated with the materials they handle, proper safety practices, and emergency procedures.
- Hazard Communication: WHMIS encourages a culture of open communication about hazards, empowering workers to ask questions and report concerns.
Understanding the Symbols: A Visual Guide to Hazards
The use of standardized symbols is a cornerstone of both HHPS and WHMIS. These symbols provide a simple and readily understandable way to communicate the potential hazards associated with a product.
Commonly Encountered WHMIS Symbols:
- Explosives: A red square with a stylized exploding bomb inside, indicating a substance that can detonate or rapidly decompose.
- Flammable: A red square with a stylized flame inside, indicating a substance that can easily ignite and pose a fire hazard.
- Oxidizer: A red square with a circle containing a stylized "O" inside, indicating a substance that can accelerate combustion or decompose explosively.
- Corrosive: A red square with a stylized hand being eaten away by acid inside, indicating a substance that can damage skin, eyes, and other materials.
- Compressed Gas: A red square with a stylized cylinder containing a gas inside, indicating a substance that is under high pressure and can cause harm if released.
- Toxic: A red square with a stylized skull and crossbones inside, indicating a substance that can cause harm through ingestion, inhalation, or skin contact.
- Biohazard: A red square with a stylized biohazard symbol inside, indicating a substance that contains biological agents that can cause disease.
- Harmful: A red square with a stylized exclamation mark inside, indicating a substance that can cause harm but is not as severe as a toxic substance.
- Irritant: A red square with a stylized exclamation mark inside and a stylized hand with a drop of liquid falling on it, indicating a substance that can cause skin or eye irritation.
- Dangerous for the Environment: A red square with a stylized tree and a drop of liquid falling on it inside, indicating a substance that can cause harm to the environment.
FAQs About HHPS and WHMIS Symbols
1. What is the purpose of the WHMIS symbols?
The WHMIS symbols are designed to provide a quick and easily recognizable visual cue to the potential hazards associated with a product. They serve as a warning to individuals handling or coming into contact with hazardous materials.
2. How are the WHMIS symbols used in the workplace?
WHMIS symbols are used on labels attached to containers of hazardous materials in the workplace. They are also included in safety data sheets (SDSs) and other workplace communication materials.
3. What should I do if I see a WHMIS symbol on a product?
If you see a WHMIS symbol on a product, it is essential to take the following steps:
- Identify the hazard: Understand the meaning of the symbol and the specific risk it represents.
- Read the label: Carefully review the label for additional information about the product, its hazards, and any necessary precautions.
- Consult the SDS: Refer to the SDS for detailed information about the product and its safe handling procedures.
- Take appropriate precautions: Follow the instructions provided on the label and in the SDS to minimize your risk of exposure.
4. Why is it important to be familiar with WHMIS symbols?
Familiarity with WHMIS symbols is crucial for ensuring workplace safety. By understanding the meaning of these symbols, individuals can quickly identify hazards, take appropriate precautions, and avoid potential accidents or injuries.
5. What are the consequences of ignoring WHMIS symbols?
Ignoring WHMIS symbols can lead to serious consequences, including:
- Accidents and injuries: Failure to recognize and address hazards can result in burns, poisoning, or other injuries.
- Environmental damage: Improper handling and disposal of hazardous materials can contaminate the environment and harm wildlife.
- Legal penalties: Employers who fail to comply with WHMIS regulations can face fines and other penalties.
Tips for Understanding and Using HHPS and WHMIS Symbols
- Familiarize yourself with the symbols: Take the time to learn the meaning of each symbol and its corresponding hazard class.
- Read labels carefully: Pay attention to the information provided on labels, including the product name, hazard symbols, and any necessary precautions.
- Consult SDSs: Always refer to the SDS for detailed information about a hazardous product.
- Ask questions: If you have any questions or concerns about a hazardous product, do not hesitate to ask your supervisor or safety officer.
- Stay informed: Keep up-to-date on any changes or updates to HHPS and WHMIS regulations.
Conclusion: The Importance of Safety Awareness
HHPS and WHMIS symbols play a vital role in promoting workplace safety and protecting the environment. By providing a clear and standardized system for communicating hazard information, these systems empower individuals to make informed decisions about their safety and the safety of others. By understanding the meaning of these symbols, taking appropriate precautions, and following established safety procedures, we can create a safer and healthier workplace for everyone.
It is crucial to remember that these systems are not merely a collection of symbols and regulations but a framework for fostering a culture of safety awareness. Through ongoing education, training, and communication, we can build a stronger understanding of the risks associated with hazardous materials and work together to prevent accidents and protect ourselves and our environment.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World of Hazardous Materials: A Comprehensive Guide to HHPS and WHMIS Symbols. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!