Navigating the World of Food Products: HSN Codes and GST Rates
Related Articles: Navigating the World of Food Products: HSN Codes and GST Rates
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World of Food Products: HSN Codes and GST Rates. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World of Food Products: HSN Codes and GST Rates
The intricate web of global trade necessitates a standardized system for classifying goods. This is where the Harmonized System (HS) code comes into play, a globally recognized nomenclature used to identify and classify traded products. Within this system, food products fall under specific HS codes, which are further refined by individual countries to create their own national tariff codes. In India, this refinement leads to the utilization of the Harmonized System Nomenclature (HSN) code, a crucial element in determining the Goods and Services Tax (GST) rate applicable to various food products.
Understanding the HSN code and its associated GST rate is paramount for businesses involved in the food industry. This knowledge empowers them to navigate the complexities of taxation, ensure compliance with regulations, and optimize their financial operations. This article delves into the intricacies of HSN codes and GST rates applicable to food products in India, offering a comprehensive guide for navigating this critical aspect of the food industry.
Decoding the HSN Code
The HSN code, a six-digit numerical code, acts as a universal language for classifying goods. It follows a hierarchical structure, with each digit representing a specific category, ultimately leading to a precise identification of the product.
For instance, the first two digits of the HSN code denote the chapter, the next two digits represent the heading, and the last two digits indicate the subheading. This systematic approach ensures clarity and consistency in product classification across various sectors, including the food industry.
Food Products and their HSN Codes
Food products encompass a vast spectrum of items, each categorized under specific HSN codes. These codes are crucial for determining the applicable GST rate and ensuring accurate tax compliance. Let’s delve into some key categories of food products and their associated HSN codes:
1. Cereals and Cereal Products (HSN Codes 1001 – 1009):
- Rice (HSN Code 1006): Unpolished, polished, parboiled, broken, or in other forms.
- Wheat (HSN Code 1001): Includes durum wheat and other varieties.
- Maize (HSN Code 1005): Includes corn flour, grits, and other forms.
- Millet (HSN Code 1008): Includes sorghum, pearl millet, and other varieties.
- Oats (HSN Code 1004): Includes rolled oats, oat flakes, and other forms.
2. Vegetables (HSN Codes 0701 – 0714):
- Fresh Vegetables (HSN Code 0701): Includes tomatoes, onions, potatoes, carrots, and other varieties.
- Frozen Vegetables (HSN Code 0710): Includes peas, green beans, spinach, and other varieties.
- Dried Vegetables (HSN Code 0712): Includes dried onions, garlic, and other varieties.
- Pickled Vegetables (HSN Code 2005): Includes pickles, relishes, and other preserved vegetables.
3. Fruits (HSN Codes 0801 – 0814):
- Fresh Fruits (HSN Code 0801): Includes apples, oranges, bananas, mangoes, and other varieties.
- Dried Fruits (HSN Code 0813): Includes raisins, dates, apricots, and other varieties.
- Frozen Fruits (HSN Code 0811): Includes strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and other varieties.
- Fruit Juices (HSN Code 2009): Includes apple juice, orange juice, grape juice, and other varieties.
4. Meat and Meat Products (HSN Codes 0201 – 0210):
- Fresh Meat (HSN Code 0201): Includes beef, pork, lamb, and poultry.
- Frozen Meat (HSN Code 0202): Includes frozen beef, pork, lamb, and poultry.
- Processed Meat (HSN Code 1601): Includes sausages, bacon, ham, and other processed meat products.
5. Dairy Products (HSN Codes 0401 – 0406):
- Milk (HSN Code 0401): Includes fresh milk, pasteurized milk, and other forms.
- Butter (HSN Code 0402): Includes unsalted and salted butter.
- Cheese (HSN Code 0406): Includes cheddar, mozzarella, parmesan, and other varieties.
- Yogurt (HSN Code 0403): Includes plain yogurt, flavored yogurt, and other varieties.
6. Fish and Seafood (HSN Codes 0301 – 0308):
- Fresh Fish (HSN Code 0301): Includes tuna, salmon, cod, and other varieties.
- Frozen Fish (HSN Code 0302): Includes frozen tuna, salmon, cod, and other varieties.
- Canned Fish (HSN Code 1604): Includes canned tuna, salmon, sardines, and other varieties.
- Shellfish (HSN Code 0307): Includes shrimp, prawns, crabs, and other varieties.
7. Confectionery and Sugar Products (HSN Codes 1701 – 1704):
- Sugar (HSN Code 1701): Includes white sugar, brown sugar, and other forms.
- Chocolate (HSN Code 1806): Includes milk chocolate, dark chocolate, and other varieties.
- Confectionery (HSN Code 1704): Includes candies, gummies, and other sweets.
8. Beverages (HSN Codes 2201 – 2209):
- Soft Drinks (HSN Code 2202): Includes cola, lemonade, and other non-alcoholic beverages.
- Fruit Juices (HSN Code 2009): Includes apple juice, orange juice, grape juice, and other varieties.
- Alcoholic Beverages (HSN Code 2204): Includes beer, wine, and spirits.
GST Rates on Food Products
The GST rate applicable to food products varies depending on the specific HSN code and the nature of the product. The GST Council has categorized food products into three main categories, each with its corresponding GST rate:
-
Zero-Rated GST (0%): This category encompasses essential food items, primarily aimed at ensuring affordability and accessibility for the general public. Examples include:
- Unprocessed cereals like rice, wheat, and millets.
- Fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Milk, curd, and buttermilk.
- Eggs.
- Fresh meat and poultry.
- Fish and seafood.
-
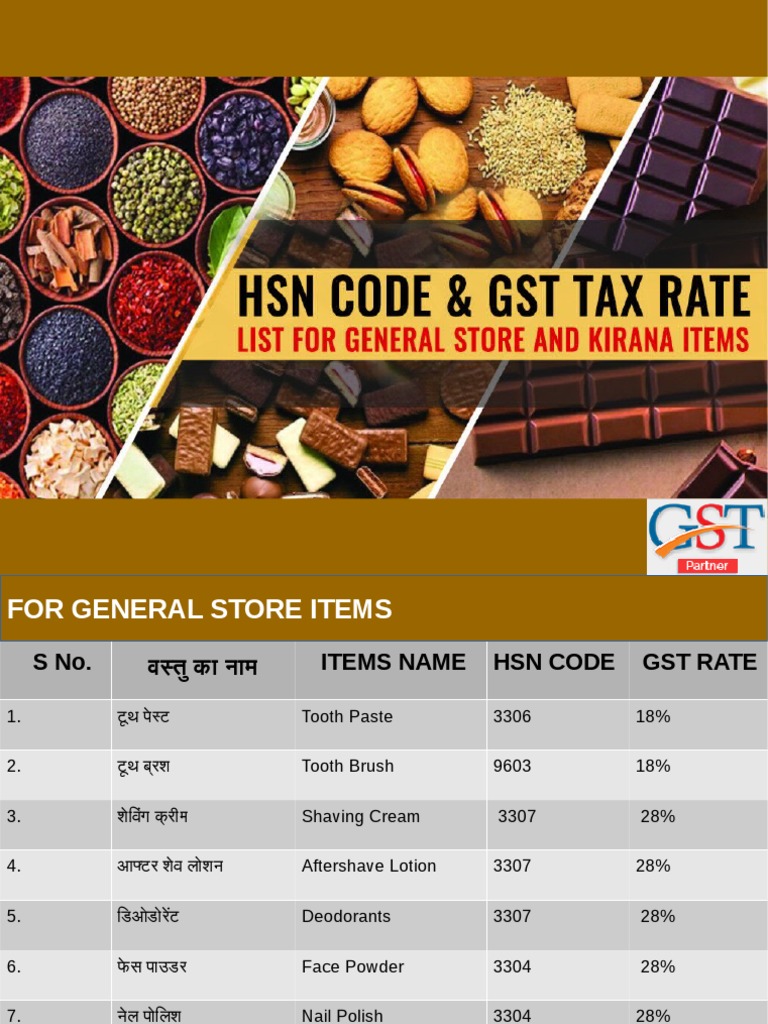
GST Rate of 5%: This category includes processed food items and other food products not covered under the zero-rated category. Examples include:
- Processed cereals like breakfast cereals and pasta.
- Canned vegetables and fruits.
- Processed meat and poultry products like sausages and bacon.
- Dairy products like cheese and yogurt.
- Processed food products like pickles, sauces, and jams.
-
GST Rate of 12% and 18%: These rates apply to specific food products like:
- Biscuits, cakes, and pastries.
- Ice cream and frozen desserts.
- Chocolate and confectionery.
- Soft drinks and other non-alcoholic beverages.
- Alcoholic beverages.
Importance of HSN Codes and GST Rates
The accurate identification of HSN codes and the application of the corresponding GST rates are crucial for businesses operating in the food industry. Here’s why:
- Tax Compliance: Ensuring the correct GST rate is applied based on the HSN code is vital for maintaining tax compliance and avoiding potential penalties.
- Accurate Invoicing: Invoices must clearly mention the HSN code of each food product, enabling seamless tracking and accounting for transactions.
- Inventory Management: HSN codes facilitate efficient inventory management by providing a standardized system for tracking and categorizing food products.
- Financial Planning: Understanding the GST implications of different food products allows businesses to make informed financial decisions and optimize their pricing strategies.
- Trade Facilitation: HSN codes streamline international trade by enabling efficient customs clearance and facilitating cross-border transactions.
FAQs
Q1. What is the difference between HSN code and GST rate?
A1: The HSN code is a six-digit numerical code used to classify goods, while the GST rate is the percentage of tax levied on a specific good or service. The HSN code determines the GST rate applicable to a particular food product.
Q2. How can I find the HSN code for a specific food product?
A2: The GST Council’s website provides a comprehensive list of HSN codes and their corresponding GST rates. You can also consult with a tax consultant or chartered accountant for assistance.
Q3. What happens if I use the wrong HSN code on my invoice?
A3: Using the wrong HSN code can lead to incorrect tax calculation and potential penalties. It is crucial to ensure accuracy when entering HSN codes on invoices.
Q4. Can the GST rate on a food product change?
A4: Yes, the GST Council can amend the GST rates on food products based on various factors, including economic conditions and policy changes.
Q5. What are the benefits of using HSN codes in the food industry?
A5: HSN codes offer numerous benefits, including tax compliance, accurate invoicing, efficient inventory management, informed financial planning, and trade facilitation.
Tips
- Stay updated: Regularly check the GST Council’s website for updates on HSN codes and GST rates.
- Seek professional advice: Consult with a tax consultant or chartered accountant to ensure accurate HSN code identification and GST rate application.
- Maintain accurate records: Keep detailed records of all transactions, including HSN codes and GST rates, for audit purposes.
- Utilize technology: Leverage accounting software and other tools to automate HSN code entry and GST rate calculation.
- Educate your staff: Ensure your employees are well-versed in HSN codes and GST rates to minimize errors and ensure compliance.
Conclusion
The HSN code and its associated GST rate are indispensable tools for businesses operating in the food industry. By understanding the intricacies of this system, businesses can ensure tax compliance, optimize their financial operations, and navigate the complexities of the food trade effectively. Staying informed about changes in HSN codes and GST rates, seeking professional advice when needed, and maintaining accurate records are crucial for success in this dynamic sector.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World of Food Products: HSN Codes and GST Rates. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!