Acids in Our Homes: Unveiling the Chemistry of Everyday Life
Related Articles: Acids in Our Homes: Unveiling the Chemistry of Everyday Life
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Acids in Our Homes: Unveiling the Chemistry of Everyday Life. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Acids in Our Homes: Unveiling the Chemistry of Everyday Life

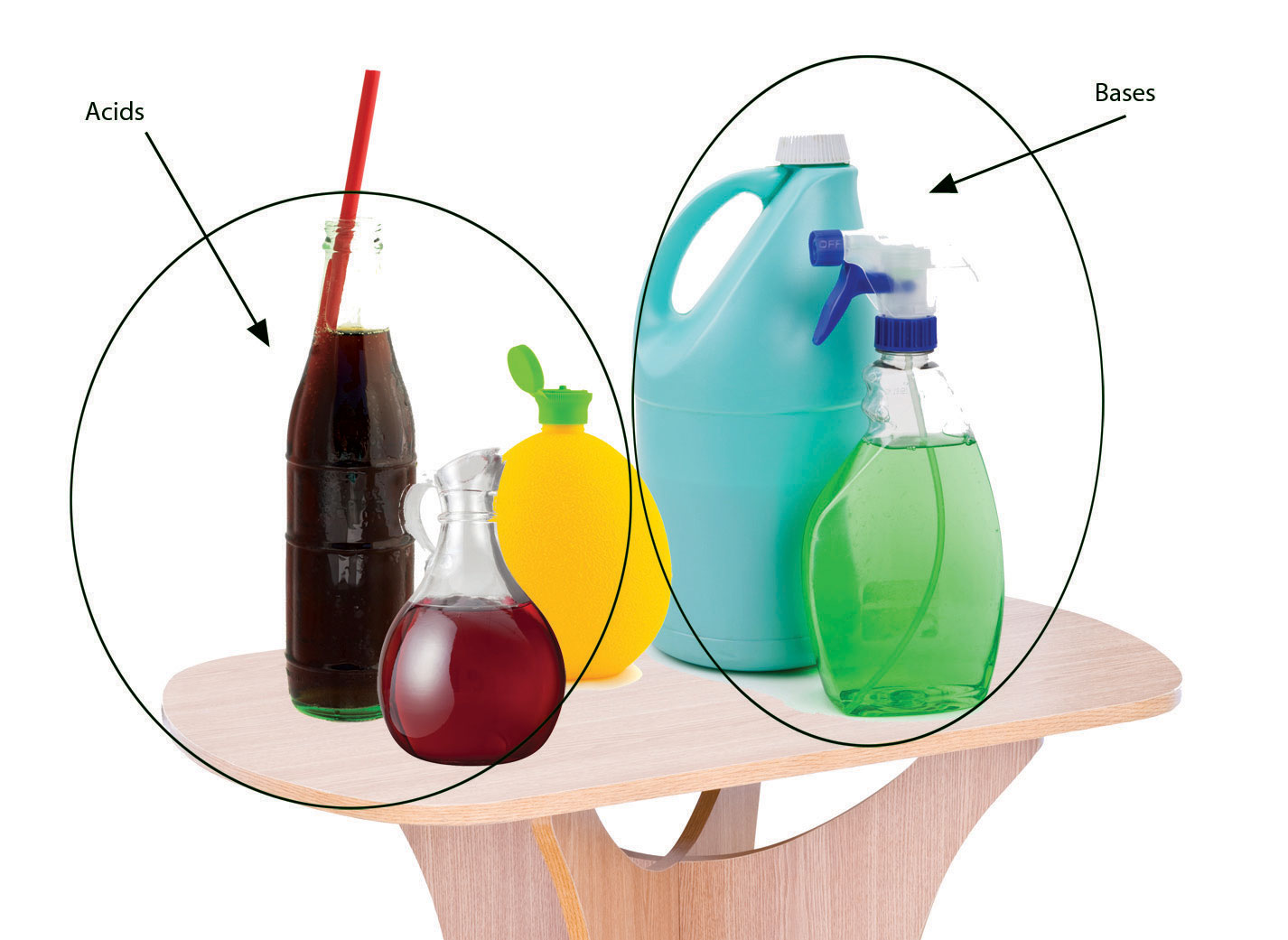
Acids, often perceived as corrosive and dangerous, are ubiquitous in our daily lives. They play a crucial role in various household activities, from cleaning and cooking to personal care. Understanding the nature of these compounds and their applications can empower us to use them safely and effectively.
A Journey into the World of Acids
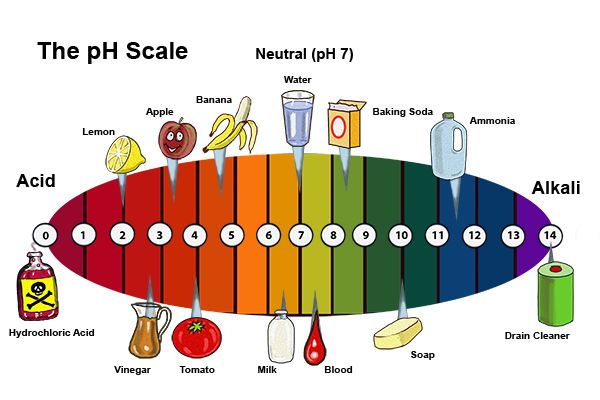
Acids are chemical substances characterized by the presence of hydrogen ions (H+) in their structure. This defining feature dictates their acidic nature, imparting a sour taste and the ability to react with bases to form salts and water.
The strength of an acid is determined by its ability to donate hydrogen ions. Strong acids, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4), readily release H+ ions, making them highly reactive. Conversely, weak acids, like acetic acid (CH3COOH) and citric acid (C6H8O7), donate H+ ions less readily, exhibiting a milder acidic character.
Everyday Encounters with Acids
While the mention of acids might conjure images of hazardous chemicals, many common household items contain acids in varying concentrations:
1. The Kitchen: A Culinary Playground of Acids
- Vinegar: A staple in many kitchens, vinegar is a dilute solution of acetic acid. Its sour taste adds zest to salads, marinades, and sauces. It also plays a vital role in preserving food, inhibiting bacterial growth.
- Lemon Juice: Rich in citric acid, lemon juice adds a tangy flavor to dishes and drinks. Its acidic properties aid in tenderizing meat and preventing browning of fruits and vegetables.
- Tomatoes: The red fruit’s tangy taste is attributed to citric acid and malic acid, contributing to its culinary versatility.
- Yogurt and Kefir: These fermented dairy products contain lactic acid, a byproduct of bacterial fermentation, which contributes to their unique texture and flavor.
- Baking Powder: This leavening agent contains sodium bicarbonate and an acidic compound like cream of tartar (potassium bitartrate) or monocalcium phosphate. When combined with water, they release carbon dioxide gas, causing baked goods to rise.
2. Cleaning Products: The Power of Acids in Maintaining Hygiene
- Toilet Bowl Cleaners: Many toilet bowl cleaners contain hydrochloric acid (HCl), which effectively removes mineral deposits and stains.
- Rust Removers: Acids like phosphoric acid and citric acid are used in rust removers to dissolve iron oxide, restoring the original metallic surface.
- Drain Cleaners: Strong acids like sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide are used in drain cleaners to break down grease and hair clogs, ensuring smooth water flow.
- All-Purpose Cleaners: Some all-purpose cleaners contain acetic acid, which acts as a disinfectant and helps remove grime and dirt.
3. Personal Care: Acids for Beauty and Hygiene
- Shampoos and Conditioners: Some shampoos contain citric acid or lactic acid to adjust pH levels and enhance hair shine.
- Skin Care Products: Alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) like glycolic acid and lactic acid are used in skin care products to exfoliate dead skin cells, promote collagen production, and reduce the appearance of wrinkles.
- Toothpaste: Some toothpastes contain phosphoric acid or citric acid to help remove plaque and tartar.
4. Beyond the Home: Acids in Our World
- Battery Acid: Lead-acid batteries, commonly found in cars, use sulfuric acid as the electrolyte, providing the electrical energy for starting the engine.
- Food Preservation: Acids like acetic acid in vinegar and citric acid in lemon juice are used to preserve food by inhibiting bacterial growth.
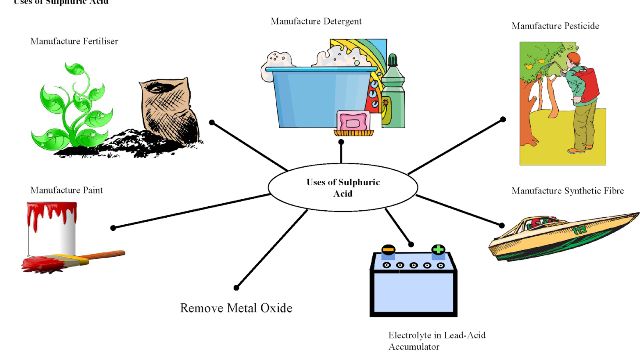
- Industrial Processes: Acids are crucial in various industrial processes, including the production of fertilizers, plastics, and pharmaceuticals.
Benefits of Acids: A Deeper Dive
While the corrosive nature of acids may raise concerns, their benefits are numerous:
- Food Preservation: Acids inhibit bacterial growth, extending the shelf life of food products.
- Cleaning and Hygiene: Acids are effective in removing dirt, grime, and mineral deposits, promoting cleanliness and hygiene.
- Health and Beauty: Acids play a role in maintaining healthy skin and hair, promoting collagen production and exfoliation.
- Industrial Applications: Acids are crucial for various industrial processes, contributing to the production of essential goods.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q1: Are all acids dangerous?
A: Not all acids are dangerous. The strength of an acid determines its potential harm. Weak acids, like those found in vinegar and lemon juice, are generally safe for household use. However, strong acids like hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid can cause severe burns and should be handled with extreme caution.
Q2: How can I safely use acids at home?
A: Always follow the instructions on product labels. Wear appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and eye protection, when handling strong acids. Store acids in well-ventilated areas, away from children and pets.
Q3: What should I do if I accidentally come into contact with an acid?
A: Immediately flush the affected area with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes. If the acid has come into contact with eyes, seek immediate medical attention.
Q4: Can I mix different acids together?
A: Mixing different acids can be dangerous, potentially leading to harmful chemical reactions. It is essential to consult product labels and safety guidelines before mixing any chemicals.
Tips for Using Acids Safely and Effectively
- Read labels carefully: Always follow the instructions provided on product labels, including safety precautions and usage guidelines.
- Wear protective gear: Use gloves and eye protection when handling strong acids, even in diluted forms.
- Store acids properly: Store acids in well-ventilated areas, away from heat and direct sunlight. Keep them out of reach of children and pets.
- Ventilate the area: Ensure adequate ventilation when using acids, especially in enclosed spaces.
- Neutralize spills immediately: If an acid spills, neutralize it with a baking soda solution and clean the area thoroughly.
Conclusion: Acids – Essential Components of Our World
Acids are integral to our daily lives, playing a vital role in food preparation, cleaning, personal care, and numerous industrial processes. While strong acids require careful handling, understanding their properties and benefits empowers us to use them safely and effectively. By following safety precautions and utilizing them responsibly, we can harness the power of acids to enhance our lives and maintain a clean and healthy environment.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Acids in Our Homes: Unveiling the Chemistry of Everyday Life. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!