A Guide to Hazard Symbols: Understanding the Language of Safety
Related Articles: A Guide to Hazard Symbols: Understanding the Language of Safety
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Guide to Hazard Symbols: Understanding the Language of Safety. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Guide to Hazard Symbols: Understanding the Language of Safety

Hazard symbols, often referred to as warning signs, play a crucial role in ensuring workplace safety and public health. These standardized pictograms convey critical information about potential risks, enabling individuals to take necessary precautions and avoid accidents. This article provides a comprehensive overview of common hazard symbols, their meanings, and their significance in promoting a safe environment.
Understanding the Importance of Hazard Symbols
Hazard symbols act as a universal language of safety, transcending language barriers and cultural differences. Their effectiveness lies in their simplicity and immediate recognition. A glance at a symbol can instantly alert individuals to potential dangers, prompting them to exercise caution and implement appropriate safety measures. This intuitive communication system is particularly vital in workplaces with diverse workforces, where language proficiency may vary.
The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS)
The GHS, developed by the United Nations, provides a standardized framework for classifying and labeling chemicals. It establishes a set of hazard symbols and signal words (such as "Danger" or "Warning") to communicate information about the hazards associated with a substance. The GHS ensures consistency across different countries, facilitating international trade and promoting a common understanding of chemical safety.
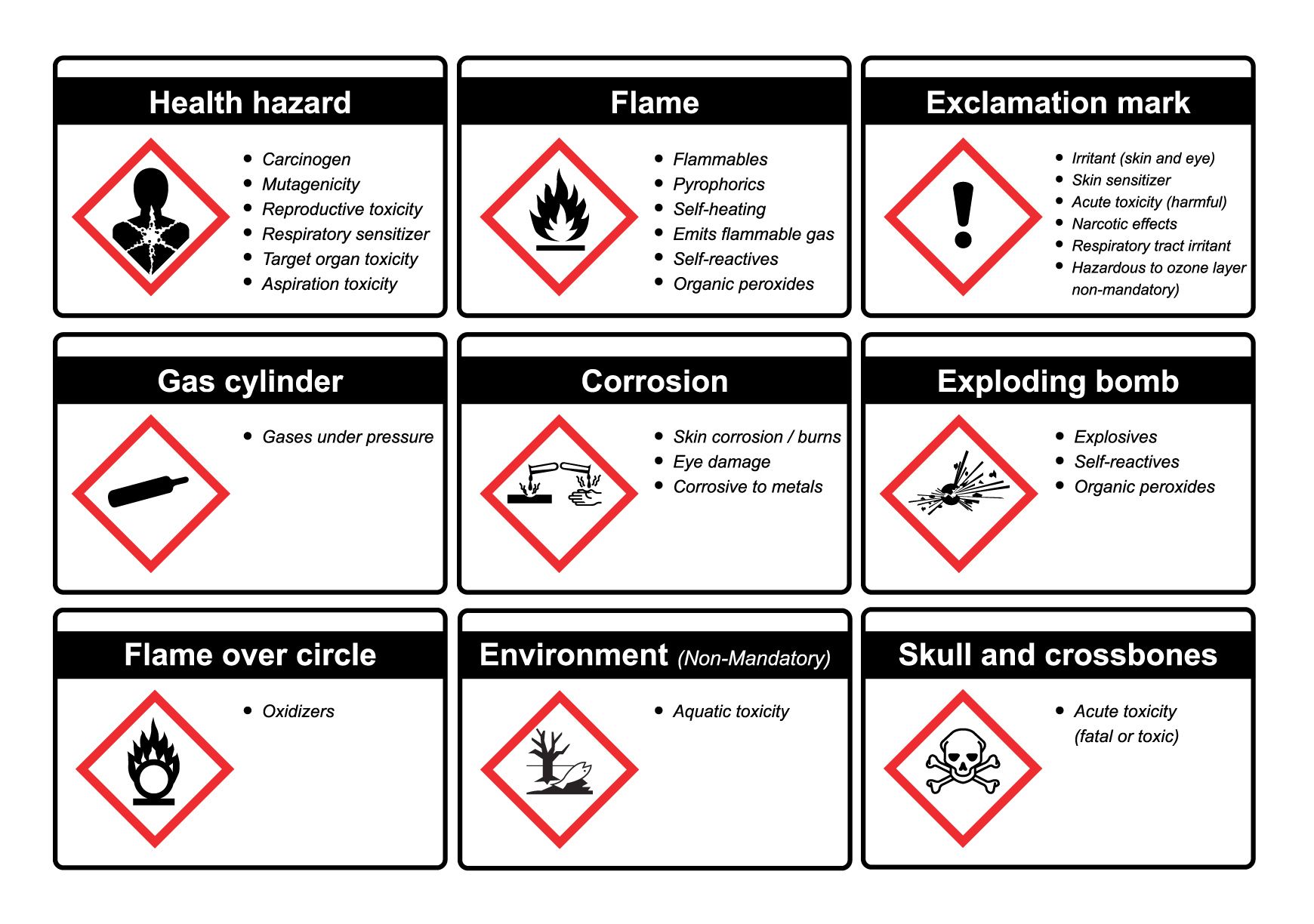
Common Hazard Symbols and Their Meanings
1. Flammable Liquids (Fire Symbol):
- Description: A flame over a circle.
- Meaning: Indicates a substance that easily ignites and burns.
- Examples: Gasoline, kerosene, alcohol.
- Safety Precautions: Keep away from heat, sparks, and open flames. Store in well-ventilated areas.
2. Flammable Solids (Fire Symbol with "S"):
- Description: A flame over a circle with the letter "S" below.
- Meaning: Indicates a solid substance that easily ignites and burns.
- Examples: Magnesium powder, sulfur, some types of plastics.
- Safety Precautions: Store in a cool, dry place away from heat and ignition sources.
3. Oxidizing Liquids (Flame over a Circle with "O"):
- Description: A flame over a circle with the letter "O" below.
- Meaning: Indicates a substance that can accelerate the burning of other materials.
- Examples: Hydrogen peroxide, nitric acid.
- Safety Precautions: Store separately from flammable materials. Avoid contact with organic materials.
4. Oxidizing Solids (Flame over a Circle with "O" and "S"):
- Description: A flame over a circle with the letters "O" and "S" below.
- Meaning: Indicates a solid substance that can accelerate the burning of other materials.
- Examples: Potassium permanganate, sodium perchlorate.
- Safety Precautions: Store separately from flammable materials. Avoid contact with organic materials.
5. Corrosive Liquids (Corrosive Symbol):
- Description: A container with drops falling from it, often with the letters "C" or "H" below.
- Meaning: Indicates a substance that can cause severe damage to skin, eyes, and other tissues.
- Examples: Acids, bases, strong detergents.
- Safety Precautions: Wear protective clothing, gloves, and eye protection. Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and mucous membranes.
6. Corrosive Solids (Corrosive Symbol with "S"):
- Description: A container with drops falling from it, often with the letters "C" or "H" below, and the letter "S" below.
- Meaning: Indicates a solid substance that can cause severe damage to skin, eyes, and other tissues.
- Examples: Calcium oxide, sodium hydroxide.
- Safety Precautions: Wear protective clothing, gloves, and eye protection. Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and mucous membranes.
7. Toxic Liquids (Skull and Crossbones Symbol):
- Description: A skull and crossbones.
- Meaning: Indicates a substance that can cause serious health problems or death if ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin.
- Examples: Cyanide, arsenic, mercury.
- Safety Precautions: Wear protective clothing, gloves, and respiratory protection. Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Do not ingest or inhale.
8. Toxic Solids (Skull and Crossbones Symbol with "S"):
- Description: A skull and crossbones with the letter "S" below.
- Meaning: Indicates a solid substance that can cause serious health problems or death if ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin.
- Examples: Lead, cadmium, asbestos.
- Safety Precautions: Wear protective clothing, gloves, and respiratory protection. Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Do not ingest or inhale.
9. Explosive Liquids (Exploding Bomb Symbol):
- Description: A bomb exploding.
- Meaning: Indicates a substance that can explode under certain conditions.
- Examples: Dynamite, nitroglycerin.
- Safety Precautions: Store in a cool, dry place away from heat and ignition sources. Handle with extreme care.
10. Explosive Solids (Exploding Bomb Symbol with "S"):
- Description: A bomb exploding with the letter "S" below.
- Meaning: Indicates a solid substance that can explode under certain conditions.
- Examples: Black powder, ammonium nitrate.
- Safety Precautions: Store in a cool, dry place away from heat and ignition sources. Handle with extreme care.
11. Compressed Gases (Gas Cylinder Symbol):
- Description: A gas cylinder with a gas escaping from it.
- Meaning: Indicates a substance that is stored under pressure and can cause harm if released.
- Examples: Oxygen, nitrogen, propane.
- Safety Precautions: Handle with care and follow manufacturer’s instructions. Use appropriate safety equipment.
12. Health Hazards (Exclamation Mark Symbol):
- Description: An exclamation mark within a triangle.
- Meaning: Indicates a substance that can cause health problems, such as skin irritation, eye irritation, or respiratory problems.
- Examples: Some solvents, pesticides, cleaning products.
- Safety Precautions: Wear protective clothing, gloves, and eye protection. Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and mucous membranes.
13. Environmental Hazards (Environmentally Hazardous Symbol):
- Description: A tree within a circle with a slash through it.
- Meaning: Indicates a substance that can cause harm to the environment, such as water pollution or soil contamination.
- Examples: Some pesticides, heavy metals, industrial chemicals.
- Safety Precautions: Dispose of properly. Avoid releasing into the environment.
14. Biohazard (Biohazard Symbol):
- Description: A circle with a stylized "biohazard" symbol (a stylized "B" within a circle).
- Meaning: Indicates a substance that contains infectious agents, such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
- Examples: Medical waste, biological samples, laboratory cultures.
- Safety Precautions: Handle with extreme care. Wear protective clothing, gloves, and respiratory protection. Follow proper sterilization and disposal procedures.
15. Radioactive Materials (Radioactive Symbol):
- Description: A stylized trifoil (three-leaf clover) symbol.
- Meaning: Indicates a substance that emits ionizing radiation.
- Examples: Uranium, plutonium, radium.
- Safety Precautions: Handle with extreme care. Wear protective clothing, gloves, and respiratory protection. Follow proper handling and disposal procedures.
FAQs about Hazard Symbols
Q: What is the purpose of hazard symbols?
A: Hazard symbols are used to warn individuals about potential dangers associated with substances or activities. They provide a quick and easy way to communicate information about risks, promoting safety and preventing accidents.
Q: Are hazard symbols standardized?
A: Yes, hazard symbols are standardized to ensure consistent communication of safety information. The GHS provides a global framework for classification and labeling of chemicals, including the use of standardized hazard symbols.
Q: Who is responsible for creating and using hazard symbols?
A: Hazard symbols are typically created and used by government agencies, regulatory bodies, manufacturers, and employers. They are essential for ensuring workplace safety, public health, and environmental protection.
Q: What should I do if I see a hazard symbol?
A: If you see a hazard symbol, take the necessary precautions to protect yourself. Read the accompanying safety information and follow the instructions provided. If you are unsure about anything, consult your supervisor or a safety professional.
Tips for Understanding and Using Hazard Symbols
- Familiarize yourself with common hazard symbols. Take the time to learn the meanings of different symbols and their implications for safety.
- Pay attention to the accompanying information. Hazard symbols are often accompanied by text or other information that provides additional details about the risks involved.
- Ask questions if you are unsure. If you are unsure about the meaning of a hazard symbol or the appropriate safety precautions, do not hesitate to ask your supervisor or a safety professional.
- Follow safety procedures. Always follow the safety procedures outlined for the specific hazard.
- Stay informed. Keep up-to-date on the latest safety regulations and guidelines related to hazard symbols.
Conclusion
Hazard symbols serve as an essential safety tool, promoting a safe and healthy environment for individuals and communities. Their standardized nature ensures consistent communication of potential risks, fostering a shared understanding of safety across diverse populations. By familiarizing oneself with common hazard symbols and their meanings, individuals can effectively mitigate risks, prevent accidents, and contribute to a safer world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Guide to Hazard Symbols: Understanding the Language of Safety. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!