A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Printing: Exploring the Possibilities and Benefits
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Printing: Exploring the Possibilities and Benefits
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Printing: Exploring the Possibilities and Benefits. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Printing: Exploring the Possibilities and Benefits
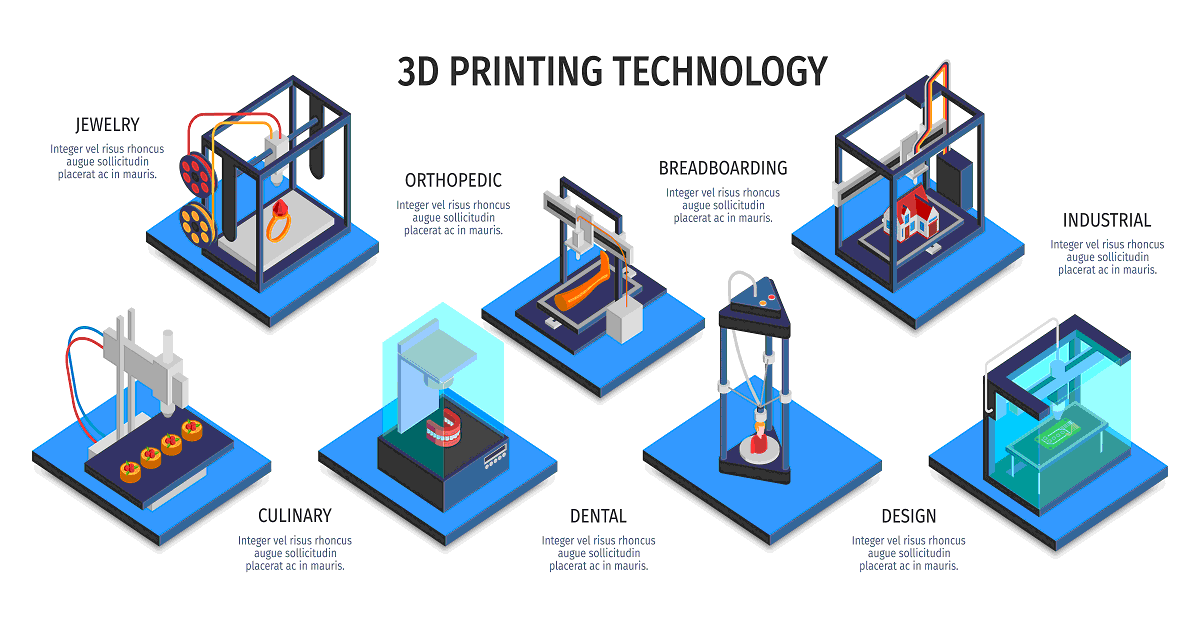
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has revolutionized the way we design, create, and manufacture objects. This technology enables the production of intricate and complex designs from a digital model, layer by layer, using a variety of materials. The versatility and accessibility of 3D printing have opened up countless possibilities for individuals, businesses, and industries alike. This article explores the diverse range of applications for 3D printing, highlighting its significance and benefits across various fields.
Exploring the Landscape of 3D Printing Applications
The realm of 3D printing encompasses a vast array of possibilities, catering to a diverse range of needs and applications. From creating personalized prototypes and intricate jewelry to building functional tools and complex medical implants, 3D printing empowers innovation and creativity across various sectors.
1. Prototyping and Design:
3D printing has become an indispensable tool for rapid prototyping and design iteration. Its ability to create physical models from digital designs allows engineers, designers, and inventors to quickly visualize and test their ideas. This iterative process accelerates product development cycles, reduces time-to-market, and fosters innovation.
Benefits:
- Reduced Time and Cost: 3D printing significantly reduces the time and cost associated with traditional prototyping methods, enabling rapid iteration and exploration of design variations.
- Enhanced Visualization and Collaboration: Physical prototypes provide a tangible representation of digital designs, facilitating better communication and collaboration among team members.
- Improved Accuracy and Detail: 3D printing enables the creation of highly accurate and detailed prototypes, capturing intricate features and complex geometries.
2. Manufacturing and Production:
3D printing is transforming manufacturing processes, enabling the production of customized and complex parts with unparalleled precision. This technology allows for the creation of intricate designs, personalized products, and on-demand manufacturing, empowering businesses to respond to evolving market demands.
Benefits:
- Mass Customization: 3D printing allows for the production of customized products tailored to individual needs and preferences, fostering a personalized consumer experience.
- On-Demand Manufacturing: The ability to print parts on demand eliminates the need for large inventory stockpiles, reducing storage costs and lead times.
- Reduced Waste and Environmental Impact: 3D printing reduces material waste by using only the necessary amount of material for each part, promoting sustainable manufacturing practices.
3. Healthcare and Medical Applications:
3D printing has revolutionized healthcare, providing solutions for personalized medicine, surgical planning, and the development of innovative medical devices. Its ability to create intricate structures and customized implants has opened up new possibilities for patient care.
Benefits:
- Personalized Medicine: 3D printing enables the creation of customized medical devices, implants, and prosthetics tailored to individual patient needs, enhancing treatment outcomes.
- Surgical Planning and Simulation: 3D printed models of patient anatomy allow surgeons to plan complex procedures, simulate surgeries, and improve surgical precision.
- Bioprinting and Tissue Engineering: 3D printing is used to create biocompatible scaffolds for tissue regeneration, paving the way for revolutionary advancements in regenerative medicine.
4. Education and Research:
3D printing provides a hands-on learning experience for students and researchers, fostering creativity, problem-solving skills, and an understanding of complex concepts. Its accessibility and affordability make it an ideal tool for educational institutions and research laboratories.
Benefits:
- Engaging Learning Experience: 3D printing allows students to design, print, and interact with physical models, enhancing their understanding of scientific principles and engineering concepts.
- Enhanced Research and Development: 3D printing enables researchers to create prototypes, test designs, and develop new materials, accelerating scientific discovery and technological advancements.
- Accessible Technology: The availability of affordable 3D printers makes this technology accessible to educational institutions and research labs, fostering innovation and scientific progress.
5. Art, Design, and Creativity:
3D printing has unleashed a wave of creativity in art, design, and architecture. Its ability to create intricate sculptures, personalized jewelry, and unique architectural models allows artists and designers to push the boundaries of their creative expression.
Benefits:
- Unique and Personalized Artworks: 3D printing allows artists to create unique and personalized artworks, catering to individual tastes and preferences.
- Innovative Design Solutions: 3D printing enables designers to experiment with complex geometries and unconventional materials, pushing the boundaries of design and aesthetics.
- Architectural Modeling and Visualization: 3D printed models provide a tangible representation of architectural designs, facilitating communication and collaboration among architects, clients, and stakeholders.
6. Aerospace and Automotive Industries:
3D printing is transforming the aerospace and automotive industries, enabling the creation of lightweight and durable parts, reducing manufacturing costs, and accelerating product development cycles.
Benefits:
- Lightweight and Durable Parts: 3D printing allows for the creation of intricate and lightweight components, reducing aircraft weight and improving fuel efficiency.
- Reduced Manufacturing Costs: 3D printing eliminates the need for expensive tooling and molds, reducing manufacturing costs and lead times.
- Rapid Prototyping and Design Iteration: 3D printing accelerates product development cycles, enabling engineers to quickly test and refine designs.
7. Consumer Products and Everyday Objects:
3D printing is increasingly used to create consumer products and everyday objects, ranging from personalized phone cases and kitchenware to toys and home décor.
Benefits:
- Personalized Products: 3D printing allows consumers to create custom-designed products that reflect their individual tastes and preferences.
- On-Demand Manufacturing: 3D printing enables the production of products on demand, reducing waste and eliminating the need for large inventory stockpiles.
- Innovative and Functional Designs: 3D printing allows for the creation of unique and functional designs, pushing the boundaries of product design and functionality.
Frequently Asked Questions about 3D Printing
Q1: What materials can be used for 3D printing?
A: 3D printing utilizes a wide range of materials, including plastics (PLA, ABS, Nylon), resins (photopolymer), metals (aluminum, steel, titanium), ceramics, and even biocompatible materials. The choice of material depends on the application and desired properties of the printed object.
Q2: How does 3D printing work?
A: 3D printing involves building a three-dimensional object layer by layer from a digital model. The process typically involves a 3D printer, a digital design file (STL or OBJ format), and a material feedstock. The printer uses a controlled process to deposit, solidify, or fuse material onto a build platform, creating the desired object.
Q3: What are the advantages of 3D printing over traditional manufacturing methods?
A: 3D printing offers several advantages over traditional manufacturing methods, including:
- Customization and Personalization: 3D printing allows for the creation of customized and personalized products.
- Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing significantly reduces the time and cost associated with traditional prototyping methods.
- Reduced Waste and Environmental Impact: 3D printing uses only the necessary amount of material, reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
- Complex Geometries and Designs: 3D printing enables the creation of intricate and complex designs that are difficult or impossible to produce using traditional methods.
- On-Demand Manufacturing: 3D printing allows for the production of parts on demand, eliminating the need for large inventory stockpiles.
Q4: What are the limitations of 3D printing?
A: While 3D printing offers numerous advantages, it also has certain limitations:
- Production Speed: 3D printing can be slower than traditional manufacturing methods, especially for large-scale production runs.
- Material Properties: The properties of 3D printed materials can sometimes differ from those of materials produced using traditional methods.
- Scale and Size Limitations: 3D printers have limitations in terms of the size and complexity of objects they can print.
- Post-Processing Requirements: 3D printed parts often require post-processing steps such as sanding, smoothing, or painting to achieve the desired finish.
Tips for Choosing the Right 3D Printer
Choosing the right 3D printer depends on your specific needs and applications. Consider the following factors:
- Printing Technology: Different 3D printers utilize different printing technologies, such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), and others.
- Material Compatibility: Choose a printer that supports the materials you intend to use for your projects.
- Print Volume and Resolution: Consider the size and complexity of the objects you plan to print, as well as the desired level of detail.
- Cost and Budget: 3D printers come in a wide range of prices, so set a budget and choose a printer that fits your financial constraints.
- Ease of Use and Maintenance: Consider the user-friendliness of the printer and the required level of maintenance.
Conclusion
3D printing has emerged as a transformative technology with vast potential across numerous industries. Its ability to create intricate designs, personalized products, and functional prototypes has revolutionized the way we design, manufacture, and innovate. From healthcare and education to manufacturing and art, 3D printing is empowering individuals, businesses, and researchers to push the boundaries of creativity and innovation. As 3D printing technology continues to evolve and become more accessible, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking applications in the years to come.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Printing: Exploring the Possibilities and Benefits. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!